Abstract:
Based on the meteorological data from 1951 to 2010 at Zhanjiang station (59658), the mean sur-face air temperature variation in time series is analyzed. The trend analysis, Mann-Kendall (M-K) mutation test and the wavelet analysis methods are used to investigate the trend, mutation and period of yearly mean surface air temperature. Major conclusions are obtained as follows: (1) Yearly mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang ranged from 22.5˚C to 24.5˚C, averaging 23.3˚C ± 0.48˚C. The linear decreasing trend is 0.097˚C/10a from 1951 to 2010. (2) At the seasonal scale, the mean surface air temperature has the maximum variation in spring (1980-1989, STD = 4.4˚C). The summer’s surface air temperature has the maximum mean value (MEAN = 28.9˚C), however, it has the smallest variation (STD = 1.3˚C in 1951-1959 and 1960-1969). (3) Yearly mean surface air temperature has a sharply increase around the year 1986. (4) Yearly mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang has the period of 2 - 3 a and 4 - 6 a.
1. 引言
进入20世纪以来,由于全球气候变暖,气候变化问题越来越受到科学家的关注。IPCC第4次报告指出,最近100年(1906~2005年)全球平均气温上升了0.74℃ [1] 。随着全球气候的变暖,区域性气温的变化对人们的生活生产以及军事活动等方面产生重要影响 [2] [3] [4] [5] 。气象学家针对区域地表气温展开了大量研究,并得到许多具有实际意义的结论 [6] [7] [8] [9] 。本文主要研究广东省湛江市1951~2010年平均气温趋势变化、年际和年代际的变化、突变检验和小波周期变化。旨在全球气候变化的大背景下,为研究区域气候变暖提供参考依据和数据支持。
2. 数据与方法
本文数据来源为1951~2010年湛江气象站(59658)日均气温、日最高(最低)气温资料。季节划分为:春季(3~5月),夏季(6~8月),秋季(9~11月)和冬季(12~翌年2月)。本文主要用到的方法有趋势分析法 [10] 、M-K突变检验 [11] 和小波分析 [12] 等方法。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 逐年变化
图1为湛江市1951~2010年年均气温的变化趋势图。从中可以看出,湛江近60年的平均气温均值为23.3℃,标准差为0.48℃,倾向率为0.097℃/10 a。总的来看,平均气温变化主要分为四个阶段:(1) 波动变化阶段(1951~1966年):在该阶段,平均气温围绕近60年的均值波动变化;(2) 逐年减小阶段(1967~1986年):在此阶段,平均气温呈现逐年减小的趋势;(3) 逐渐增加阶段(1987~2000年):在该阶段,平均气温为逐年增加的趋势;(4) 波动减小阶段(2001~2010年):由于2008年和2010年为冷年,造成在此阶段,平均气温在全球变暖的大背景下,呈现出波动减小的趋势。
3.2. 季节和年均年代际变化
表1为湛江1951~2010年四季和年平均气温的年代际变化。从该表可以看出,在季节变化上,春季
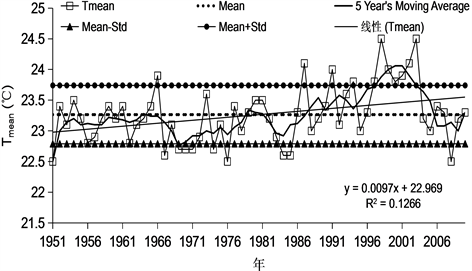
Figure 1. Variation of mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang (1951-2010), unit: ˚C
图1. 湛江年平均气温变化(1951~2010),单位:℃

Table 1. Variations of seasonal and annual decadal mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang, unit: ˚C
表1. 湛江季和年平均气温年代际的变化,单位:℃
的平均气温变化幅度最大(1980~1989年代,STD = 4.4℃),夏季的均值最大(1990~1999年代,MEAN = 28.9℃),但变化幅度却最小(1951~1959和1960~1969年代的STD = 1.3℃)。对于全年的变化而言,1990~1991年代的均值最高(MEAN = 23.6℃),平均变化幅度最大出现在1980-1989年代(STD = 5.6℃)。
3.3. M-K突变检验
Mann-Kendall (M-K)方法是一种非参数检验方法,其优点是不需要样本遵循一定的分布,也不受少数异常值的干扰。利用M-K方法对时间序列进行突变分析,以考察不同时间尺度上的突变状况。图2为1951~2010年的M-K突变检验曲线,UF为ET0顺序列的统计变化曲线,UB为逆序列的统计变化曲线,并且根据给定的显著水平α = 0.05计算出M-K检验统计量所对应的两条临界直线Zɑ = 1.96和−Zɑ = −1.96。从图2中可以看出,曲线UF和UB在1986年左右相交于两条临界曲线之间,随后曲线UF逐渐上升,至2000年,超出了临界直线Zɑ = −1.96,随后UF波动下降。通过分析,湛江平均气温在1986年前后发生一次增加的突变(与前面分析的四个阶段的特征结论一致)。
3.4. 小波分析
本文利用Morlet小波方法对1951~2010年湛江平均气温进行周期分析,以考察不同时间尺度的周期变化特征。图3为我国西北地区1951~2010年湛江平均气温年均值序列的Morlet小波功率谱,其中,黑

Figure 2. M-K test of the mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang from 1951 to 2010
图2. 1951~2010年湛江市平均气温M-K检验

Figure 3. Wavelet analysis of mean surface air temperature in Zhanjiang from 1951 to 2010
图3. 1951~2010年湛江市平均气温小波分析
色粗实线圈出的部分为置信度95%的红噪声检验,带圈的实线(COI:Cone of Influence,影响锥)以下区域受边际效应的影响功率谱减小。小波变换图中蓝色等值线表示负值,代表要素值偏低;绿至红色等值线表示正值,代表要素值偏高。小波分析的结果显示,湛江平均气温存在多重时间周期尺度的嵌套复杂结构。可以看出,湛江年均气温存在2~3 a的和4~6 a的显著性震荡周期。其中,2~3 a的震荡周期主要出现在1960~1980年代,4~6 a的震荡周期主要出现在1985~2009年。值得注意的是,在超过32年的分析中,没有闭合的中心,由于平均气温时间序列仅为60年,超过30年的周期不能明显地表示出来。
4. 结论
(1) 湛江近60年的平均气温均值为23.3℃,标准差为0.48℃,倾向率为0.097℃/10 a。其变化主要分为四个阶段:波动变化阶段(1951~1966年),逐年减小阶段(1967~1986年),逐渐增加阶段(1987~2000年)和波动减小阶段(2001~2010年)。
(2) 在季节变化上,春季的平均气温变化幅度最大(1980~1989年代,STD = 4.4℃),夏季的均值最大(1990~1999年代,MEAN = 28.9℃),但变化幅度却最小(1951~1959和1960~1969年代的STD = 1.3℃)。
(3) M-K检验结果表明,湛江平均气温在1986年前后发生一次增加的突变。
(4) 小波分析结果表明,湛江年均气温存在2~3 a的和4~6 a的显著性震荡周期。