1. 引言
亚甲基蓝(C₁₆H₁₈ClN₃S)是一种吩噻嗪盐,广泛用作化学指示剂、染料、生物染色剂等。亚甲基蓝染料废水很难降解,有着抗光解、抗生化和抗氧化等特点,长期滞留在水中,会危害人类健康和生态环境 [1] 。传统的处理工艺难以达到较好的降解效果,如何有效且低成本地处理染料废水已成为一项重要的课题。近年来,电化学法在国内外备受关注,电化学技术兼有电化学氧化、电化学还原、絮凝和气浮四种作用,具有去除污染物种类多、去除效率高、二次污染物较少、工艺和设备简单、可操控性好等诸多优点,是一种良好的绿色处理技术 [2] ,已应用于越来越多的难降解工业废水的处理 [3] 。电极材料是电化学处理的核心 [4] ,在常用的电极材料中,钢板电极是一种具有一定特性且价格低廉的常用阴极材料,当作为阳极材料时,兼有类芬顿电化学氧化反应和电絮凝的优良特点。
亚甲基蓝作为一种典型的活性染料分子,正电荷不稳定,具有较强的电化学活性 [5] 。本文采用钢板作电极,硫酸钠作电解质,对亚甲基蓝模拟废水进行电化学处理,通过单因素条件实验得到最佳工艺参数,采用GC-MS、IC分析手段,检测在最佳工艺条件下电解后的中间产物,分析亚甲基蓝可能的降解途径。
2. 试验部分
2.1. 试剂与仪器
试剂:亚甲基蓝(国药集团化学试剂有限公司),硫酸钠(西陇化工股份有限公司),均为分析纯;二氯甲烷(天津市光复精细化工研究所,色谱纯)试验用水为蒸馏水。
仪器:GPS-4303C型多组输出直流电源(固纬电子有限公司),722型可见分光光度计(天津市普瑞斯仪器有限公司),HJ-4A多头磁力加热搅拌器(广州沪瑞明仪器有限公司),GC7890A/MS5975C (Agilent Technologies),Vario TOC (Elementar),ICS-1100 (戴安中国有限公司)。
2.2. 溶液配制
亚甲基蓝模拟废水由亚甲基蓝和去离子水配置而成,准确称取亚甲基蓝粉末2.0000 g于烧杯,溶解后,置于2000 mL的容量瓶中定容,浓度为1000 mg/L,实验时稀释至相应浓度。
2.2.1. MB的测定
用量筒量取200 mL模拟废水倒入250 mL烧杯中,加入一定量的Na2SO4电解质,不改变原水PH值,在室温下进行相关试验。间隔一定时间取样,经离心沉淀后取上清液稀释适当倍数,用分光光度计测定其吸光度(以去离子水为参比),参照标准曲线,确定待测液浓度,计算去除率。
2.2.2. 中间产物分析
中间产物用气相色谱–质谱GC7890A/MS5975C分析,色谱柱DB-5,升温程序如下:40℃,保持2 min,以20℃/min升到280℃,保持15 min,再以10℃/min升到320℃。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1. 钢板电极电化学处理亚甲基蓝模拟废水的工艺条件优化
研究表明,电解时间、外加电压、极板间距、电解质浓度、PH值、废水初始浓度都会影响污染物的去除效率。因此,本试验选择外加电压、极板间距、电解质浓度和MB初始浓度为主要考察因素,利用钢板电极对MB模拟废水进行单因素条件试验。
3.1.1. 外加电压的影响
MB初始质量浓度100 mg/L,电解质Na2SO4浓度0.05 mol/L,极板间距1.5 cm,搅拌速度150 r/min,室温条件下考察外加电压对亚甲基蓝去除率的影响,结果如图1所示。
由图1可知,随着外加电压的增大,亚甲基蓝去除率逐渐升高。试验过程中,亚甲基蓝被电极表面析出的活性氧及羟基自由基氧化降解。外加电压为5 V时,电化学处理120 min,MB去除率为75.33%;外加电压为9 V时,电解120 min,MB去除率可达85.19%。由于外加电压的增大,导致模拟废水中的
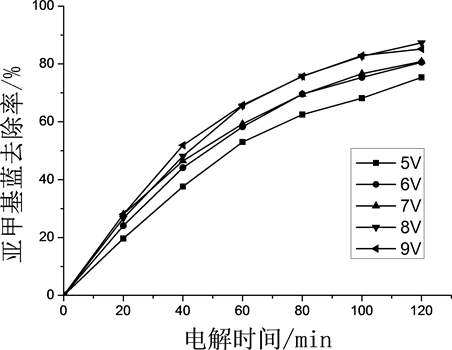
Figure 1. Effect of applied voltage on MB removal rate
图1. 外加电压对MB去除率的影响
电流增大,增大了带电粒子运动的推动力,使电荷与亚甲基蓝分子接触的机会增多,电子转移速率加快,电极表面发生氧化反应的速率加快,有利于电化学反应的进行。随着试验的进行,可明显观察到溶液中暗绿色絮状体增多,电极表面气泡增多,气浮作用明显。当外加电压为8 V时,电解120 min,MB去除率可达87.29%,比9 V时的处理效果稍好;从理论上讲,外加电压越大产生的∙OH浓度越高,一定时间内电解反应越迅速,MB的去除率越高。但外加电压过大,副反应也同时加剧,单位时间内的电极上产气量增多并汇聚成较大气泡,由于所产生气体沿极板上升,减少了极板电化学反应的有效比表面积,降低了电化学处理效果。随着外加电压的增大,电流过大,本来寿命很短的∙OH不能很稳定存在,故选择8 V为最佳电压。
3.1.2. 极板间距的影响
MB初始质量浓度100 mg/L,电解质Na2SO4浓度0.05 mol/L,外加电压为8 V,搅拌速度150 r/min,极板间距分别为1 cm、1.5 cm、2.0 cm、2.5 cm,室温条件下,考察极板间距对亚甲基蓝模拟废水去除率的影响,结果如图2所示。
图2曲线表明,随着极板间距的增大,亚甲基蓝的去除率逐渐下降,这是因为当外加电压一定时,电场强度随着极板间距增大而减小,进而增加了对流、扩散传质的距离,废水中有机物分子的电迁移速率减慢。极板间距为1 cm时,电解120 min,MB去除率为87.99%;极板间距为1.5 cm,电解120 min,MB去除率为87.29%,与间距为1 cm时相差不大。极板间距较小时,浓度差极化的影响较小,超电势随之降低,处理效果较好。虽然极板间距越小去除率越高,但过小的极板间距会使极板间溶液的流量减小、废水温度升高,极板间电场过强,存在通电瞬间极板间放电的危险,降低极板的使用寿命。此外,在实际工艺中,极板间距过小也会提高电解装置的设计要求。综合考虑各因素,选择1.5 cm作为适宜极板间距。
3.1.3. 电解质浓度的影响
MB初始质量浓度为100 mg/L,外加电压8 V,极板间距为1.5 cm,电解质浓度分别为0.03 mol/L、0.04 mol/L、0.05 mol/L、0.06 mol/L、0.07 mol/L;室温条件下,考察电解质浓度对MB去除率的影响,结果如图3所示。
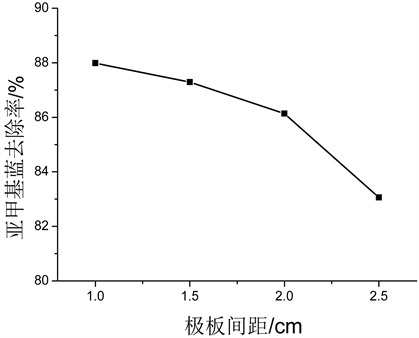
Figure 2. Effect of plate spacing on MB removal rate
图2. 极板间距对MB去除率的影响

Figure 3. Effect of electrolyte concentration on MB removal rate
图3. 电解质浓度对MB去除率的影响
电解质的加入可以增加溶液的导电性能,也可以使电解过程中发生复杂的电化学反应;由图3可知,随着电解质Na2SO4浓度的增大,亚甲基蓝的去除率呈现先增大后减小的趋势。当其浓度从0.03 mol/L增加到0.05 mol/L时,电化学处理120 min,MB去除率从82.94%增长到87.29%,去除效果提高了4.35%。外加电压不变的条件下,随着电解质浓度的增加,电流增大,废水的导电能力也随之增强,有利于亚甲基蓝的氧化降解。当电解Na2SO4浓度超过0.05 mol/L时,电解质浓度太大而不利于废水中的电化学反应进行,从而降低了反应速率,影响了MB的去除率,故选择最佳电解质浓度为0.05 mol/L。
3.1.4. 模拟废水初始浓度的影响
外加电压为8 V,极板间距1.5 cm,电解质浓度为0.05 mol/L,模拟废水初始浓度分别为50 mg/L、100 mg/L、150 mg/L、200 mg/L、250 mg/L、300 mg/L、400 mg/L;室温条件下,考察MB初始浓度对去除率的影响,结果如图4所示。
由图4可知,当废水的初始浓度从100 mg/L增加到300 mg/L时,电解处理120 min,MB的去除率随初始浓度的增大而逐渐提高,最高可达94.65%;MB初始浓度较低时去除率并不高,可能是由于亚甲基蓝不断被降解,单位时间内扩散到电极表面的亚甲基蓝减少,影响了亚甲基蓝在电极表面的氧化降解。当MB浓度继续增大到400 mg/L时,电解120 min,电化学处理效果反而降低,MB去除率为92.80%。这可能是由于在试验范围内,钢板电极的电化学作用随初始浓度的升高而增大,降解、破坏的MB分子成正比增加;当初始浓度过高时,高浓度的亚甲基蓝能较快地扩散到电极表面并发生反应,但随着反应的进行,更多的反应产物堆积在电极表面,阻碍了传质过程,使电流效率降低;也可能是由于电化学作用达到饱和,在相同的反应时间内,作用在单位浓度污染物上的∙OH含量减少,导致去除效果降低,故本试验确定MB模拟废水的最佳初始浓度为300 mg/L。
3.2. 电场作用下亚甲基蓝溶液中的TOC变化
对于TOC值的变化,可以将整个过程大致分为两个阶段:第一阶段为亚甲基蓝分子分解为小分子有机物,此阶段亚甲基蓝分子发色基团被破坏;第二阶段为深度氧化阶段,此阶段溶液中的有机物分子被快速的矿化为无机盐离子、CO2和H2O。由图5可知,随着电解时间的延长,亚甲基蓝溶液的TOC值

Figure 4. Effect of initial concentration on MB removal rate
图4. 初始浓度对MB去除率的影响
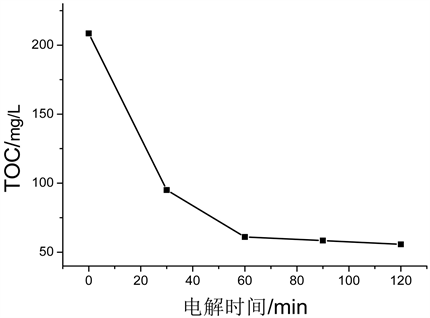
Figure 5. TOC variation curve under electric field
图5. 电场作用下TOC变化曲线
呈现递减的趋势;且在60 min之前,TOC下降速率较快,反应继续延长至120 min时,TOC的去除率可达73.28%。这表明此反应中大部分亚甲基蓝分子被完全矿化,部分未被完全矿化的亚甲基蓝分子被氧化分解为小分子中间产物。
4. 降解机理分析
4.1. 主要的化学反应
在电解反应过程中有微量的暗绿色絮体和气泡产生,其可能发生如下的电化学反应 [6] [7] [8] :
反应一阳极:
阴极:
反应二阳极:
阴极:
上述反应后产生铁的氢氧化物絮状体,通过吸附混凝或络合作用从而去除亚甲基蓝。此外,在阳极伴有水氧化的竞争析氧反应,该反应主要存在类电芬顿过程:
阳极:
阴极:
4.2. 降解产物分析
化学反应是旧键的断裂和新键的生成过程,亚甲基蓝分子中的化学键能 [9] 见表1所示。
马文姣等 [10] 研究了在声化学和电化学共同作用下,亚甲基蓝一方面中间环的碳氮键先被打断,甲基脱落,氧化成环己基-3-二(甲基氨基)苯基甲酮(C15H21ON),继而氧化成环己基苯基甲酮(C13H18O);另一方面碳氮键断开生成2-氨基苯基硫代苯胺(C12H12N2S),进一步氧化成3-异氰酸酯基苯酚(C7H5O2N);最终氧化成苯甲酸、甲酸、乙酸、乙二酸等小分子酸。Qianwang等 [11] 研究了在二茂铁多相催化类芬顿反应体系中,亚甲基蓝可能有三种不同的降解途径:1) MB分子中能量最低的N-CH3首先被破坏,进而氧化生成甲醛或者甲酸;2) 碳硫键和碳氮键被打断氧化生成苯并噻唑;3) Cl-S被氧化成S=O,进一步氧化生成苯胺-2-磺酸;随着反应的进行,这些产物最终被氧化成CO2、H2O、
和
。
本试验在电场作用下电解亚甲基蓝模拟废水,随着电化学反应的进行,亚甲基蓝浓度逐渐降低,这表明亚甲基蓝的分子结构或发色基团遭到了破坏。通过GC-MS、IC检测出电化学反应的中间产物,见表2和图6所示。
据测得的中间产物根,分析该条件下亚甲基蓝可能存在2条不同的降解途径,如图7所示。反应进行时,Cl−游离在溶液中,电化学反应产生的自由基破坏亚甲基蓝中间环碳硫键和苯环上碳氮键,氧化生成
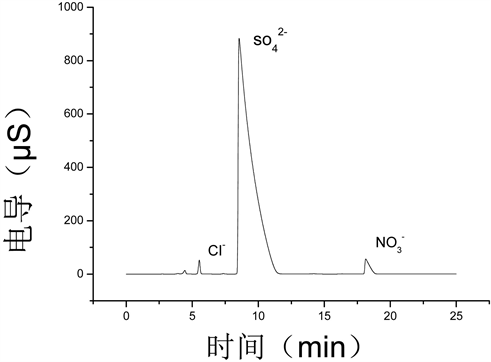
Figure 6. The inorganic anion in the MB solution after electrolysis for 120 min
图6. 电解120 min后MB溶液中的无机阴离子

Table 1. Chemical bond energies in the molecular structure of methylene blue
表1. 亚甲基蓝分子结构中的化学键能

Table 2. Possible intermediate products under electrochemical conditions
表2. 电化学条件下可能的中间产物

Figure 7. Possible degradation pathways of methylene blue under electrochemical action
图7. 电化学作用下亚甲基蓝可能的降解路径
2-甲基-5,5-二苯基-4-甲硫基咪唑(B);亚甲基蓝分子中键能最低的化学键CH3-N(CH3)C6H5为70.8 (kcal/mol),因此,部分甲基可能首先脱落,被氧化成甲醛或甲酸。自由基继续破坏B物质上的碳硫键、碳氮键以及咪唑与苯环之间的碳碳键,生成3-氨基-1,2-苯并异噻唑(C)和物质E;随着电化学反应的继续进行,C物质上氨基可能脱落生成苯并噻唑,E物质会生成F以及它的同分异构体G,进而可能氧化成苯酚,最终矿化为
、CI−、
、CO2、H2O等小分子化合物。此外,电化学反应过程中产生的羟基自由基与大多数有机污染物可以发生快速的链式反应,无选择性地把废水中有机污染物氧化成CO2、H2O和简单的有机化合物 [12] ,处理过程不产生或基本不产生二次污染。
5. 结论
1) 钢板电极电化学处理MB模拟废水的最佳条件为:MB初始质量浓度300 mg/L,外加电压8 V,极板间距1.5 cm,电解质(Na2SO4)浓度0.05 mol/L,电解时间120 min。在此最佳工艺条件下,MB去除率可达94.65 %,TOC去除率可达73.28%。
2) 钢板电极电化学处理MB可能的降解途径为:a) MB甲基首先脱落,氧化成甲醛或甲酸等小分子酸;b) MB的碳氮键和碳硫键被破坏生成2-甲基-5,5-二苯基-4-甲硫基咪唑,随之氧化生成噻唑和酚类化合物,最终矿化为
、CI−、
、CO2、H2O等小分子化合物。
基金项目
湖北省自然科学基金(2012FFB04703);湖北省自然科学基金(2014CFB411);武汉工程大学研究生创新基金(CX2016159)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。