1. 引言
湿地是介于陆地和水生环境之间的过渡区域 [1] [2] ,具有保护物种和遗传多样性、减缓地表径流、防止水土流失、调节区域气候及美化环境等功能 [3] [4] 。然而近年来,随着经济快速发展、人口持续增长、城市化进程加快以及环境污染加剧,世界各国的天然湿地不同程度地发生退化,甚至遭到破坏。湿地面积减少和富营养化加剧是威胁湿地生态系统的两大主要问题 [5] 。美国从殖民时期以来,大约有53%的天然湿地已经消失 [6] 。我国由于长期以来湿地的效益和功能并未得到社会公众和政府部门的重视,造成湿地盲目开发,湿地面积和湿地资源也日益减少 [7] ,湖泊水环境氮磷污染引起的富营养化问题更为严重。国内外现状调查结果表明,在全球范围内已有30%~40%的湖泊和水库遭受不同程度富营养化影响 [8] 。近年来湖泊富营养化呈上升的趋势,据统计,在我国131个大型湖泊湿地中,达到富营养化程度的湖泊已经有67个,占比超过50% [9] 。
由于氮磷水环境污染问题较为严重,其治理措施也已经成为国内外学者研究的重点问题。如郑建初等 [10] 用水葫芦来治理太湖流域水体氮磷污染,提出了水葫芦治理措施关键措施和确保治理效果新机制。李旭东等 [11] 通过沸石床处理农田暴雨径流中的氮磷污染物,对总氮和总磷的去除率可达45%和38%。欧美国家主要对引起氮磷污染的农业进行污染源控制,对点源污染主要通过兴建污水处理工程进行末端控制,已取得较好成效,而对面源污染主要通过农田最佳养分管理等农业措施削减氮、磷总量 [12] 。氮磷水环境污染问题由于分布面广、污染程度不一,目前并没有适用各种环境且一劳永逸的治理措施,需要根据不同的污染源和污染特点制定相应的措施来缓解其带来的负面影响。
洞庭湖一直是国内学者研究的热点区域。以往对洞庭湖研究主要集中在进出湖泊径流和泥沙特征分析 [13] 、水沙丰枯遭遇频率分析 [14] 、沉积物重金属污染 [12] [13] 等方面,如Chang等 [15] 对三峡工程建设前后洞庭湖泥沙淤积特征、空间分布及变异规律进行了系统的分析与总结;Hu等 [16] 和Liang等 [17] 分别分析了洞庭湖铬(Cr)、铜(Cu)、铅(Pb)等重金属的来源和污染风险。而关注湿地演替带氮磷迁移转化规律的研究相对较少,且缺少对洞庭湖地表水和地下水氮磷污染物监测长期数据。氮磷超标引起的水体富营养化问题已经严重威胁到洞庭湖区居民的饮用水安全与社会稳定 [18] [19] 。为了揭示洞庭湖富营养化的发生机制与蓝藻暴发的机理,必须查清地表水和地下水体中氮、磷的时空分布特征及其变化规律。因此,本文以西洞庭湖为研究对象,探索水体中氮、磷等营养盐的时空分布特征及其环境效应,为洞庭湖湿地富营养化治理提供理论支撑和技术支持。
2. 研究区概况
洞庭湖是我国第二大淡水湖,位于湖南省北部,长江荆江河段南岸,地理坐标位置为东经111˚14'~113˚10',北纬28˚30'~30˚23',由东、南、西洞庭湖和大通湖4个较大湖泊以及密集的河网水系组成。该区属中北亚热带湿润气候区,年平均气温16.4℃~17℃,无霜期258~275 d,年降水量1100~1400 mm,6~9月降雨占年降水总量50%以上,多为大雨和暴雨,易形成洪、涝、渍灾害。洞庭湖区有湘江、资江、沅水、澧水4大河流,水系流域面积262 800 km2。洞庭湖是典型的吞吐型湖泊,与长江相通,通过松滋口、太平口、藕池口、调弦口(1958年封堵)四口分流入湖,入湖水经洞庭湖调节后从城陵矶出口重新汇入长江。洞庭湖区地势平坦,土地集中,土壤肥沃,适宜于多种作物生长,得天独厚的自然环境给当地社会经济发展提供了优厚的物质基础。建国以来,湖区经济日益发展,成为湖南省的粮、鱼、棉基地,也是全国重要的商品粮、渔业基地。
3. 研究方法
3.1. 监测方案与样品采集
研究区域为西洞庭湖澧水和沅水入湖口湿地演替带,其中澧水湿地演替带为农田区,种植有大量农作物,而沅水演替带为土壤裸露区,地表生长少量杂草。在澧水和沅水入湖口湿地演替带选取试验场地,位置如图1所示。在每个试验场地各布置2个与湖岸垂直的监测剖面,分别为L-T1、L-T2和Y-T1、Y-T2,剖面间距320m。在每个剖面布置3个监测钻孔,孔间距为30 m,共12个,孔深为8.00~12.50 m不等,其中澧水监测孔编号为L-1~L-6,沅水监测孔编号为Y-1~Y-6。监测点位置及编号如图2所示。监测周期为1个水文年,水样采集时间从2014年6月至2015年5月,每月25日左右采集一次地表水和地下水样。为保证地下水样的代表性,在地下水位以下0.5 m取样,用专业有机玻璃采水器进行采集。将采集的水样进行编号,及时送实验室进行三氮浓度(
,
和
)及磷酸盐(
)浓度分析。
3.2. 测定方法
硝酸盐氮(
)、亚硝酸盐氮(
)和铵态氮盐(
)分别采用麝香草分光光度法、重氮偶合分光光度法和钠氏剂分光光度法测定,磷酸盐(
)采用磷钼蓝分光光度法测定。所有水样采集后立即送回实验室进行样品处理,每500 mL水样中添加0.4 mL硫酸,并5℃环境下保存,24小时内完成规定项目检测工作。其中,硝酸盐氮(
)测定的相对标准偏差为3.8%,相对误差为1.4%;
相对偏差小于2.8%,
的相对标准偏差为6%,相对误差为0。磷酸盐(
)测定的相对标准偏差为8.3%,相对误差为6.6%。
4. 监测结果分析与讨论
4.1. 三氮分布特征
湿地演替带地下水中
时空分布特征如图3所示。在时间分布上,澧水演替带地下水中
在0.7 mg/L附近上下波动,沅水演替带地下水中2014年6月和2015年2~5月
浓度略高于检测极限值,其余时段内地下水中的
浓度一直在0.5645 mg/L左右,说明沅水演替带地下水中的
浓度一直较低。在空间分布上,除了2014年6月份沅水演替带地下水中
浓度略大于澧水外,其余时间均是澧水演替带地下水中
浓度较高,而且在丰水期浓度差有加大的趋势,而在枯水期有减小的趋势。
演替带地下水中
时空分布特征如图4所示。在时间分布上,两个演替带中各自在6月和7月
浓度出现了极大值,其中6月澧水地下水中
浓度为0.0526 mg/L,而沅水地下水中只有0.0085 mg/L,二者相差6倍;在7月沅水地下水中
浓度为0.0647 mg/L,而澧水地下水中只有0.0047 mg/L,二者相差将近14倍。说明在6、7月份微生物活动较频繁,硝化和反硝化反应也较强烈,生成的中间产物
较多,从而使
得到了一定的积累。
浓度的空间分布并不像
那样,澧水浓度普遍高于沅水中的浓度,澧水和沅水中
浓度交替增加或减小或浓度相等。根据《地下水质量标准GB/T14848-93》得出两个演替带地下水根据
分类90%都属于II类水(如图4中红线标识),地下水受
污染程度较小。

Figure 1. The location of sampling site
图1. 采样点地理位置

Figure 2. The layout of sampling wells (The sampling wells are L-1~L-6 in Li River, and are Y-1~Y-6 in Yuan River)
图2. 采样点布置图(澧水监测孔分别标号为L-1~L-6,沅水监测孔分别标号为Y-1~Y-6)
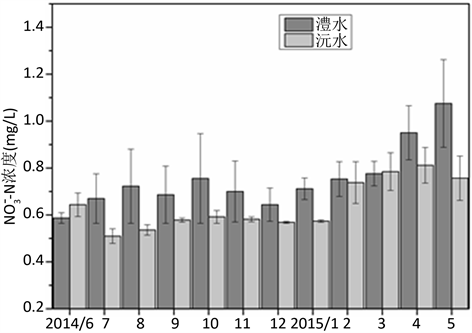
Figure 3. The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of
图3. 演替带地下水
时空分布特征

Figure 4. The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of
图4. 演替带地下水
时空分布特征
演替带地下水中
时空分布特征如图5所示。在时间分布上有如下特点,澧水演替带地下水中在6月份为2014年试验段内的最高值,为3.2109 mg/L。沅水演替带中6月
浓度也很高,为2.3411 mg/L。从空间角度分析,澧水演替带地下水中的
浓度在大部分时间内都大于沅水地下水中的浓度,说明澧水地下水中
污染程度要比沅水严重。这主要是澧水试验区内2月是油菜施肥高峰期,大量的施肥引起地下水中
浓度的突然增加,引起的高浓度
污染,而
和
浓度也都是在2、3月浓度突然增加,说明
在地下环境中发生了硝化反应,但略有迟滞现象。
4.2. 磷酸盐分布特征
澧水和沅水演替带中磷酸盐时空变化如图6所示。澧水和沅水2014年7月
大幅下降,2015
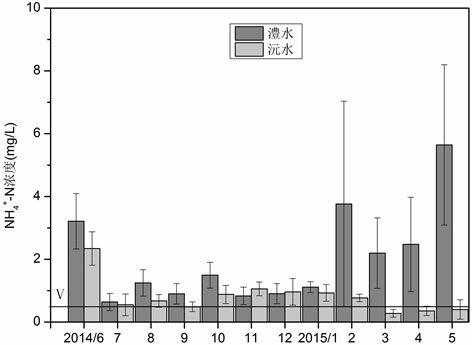
Figure 5. The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of
图5. 演替带地下水
时空分布特征
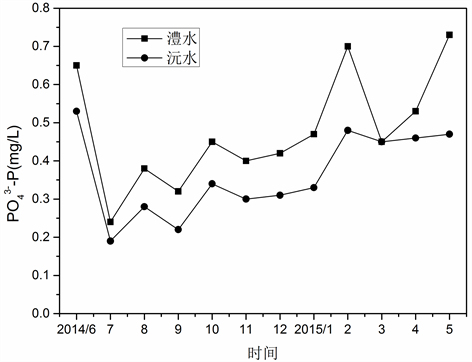
Figure 6. The spatial-temporal distribution characteristics of
图6. 演替带磷酸盐时空分布特征
年8月至201年2月有略微增加的趋势,特别是在2015年2月增幅较大。在2015年3月都有减小的趋势,4月和5月
浓度都有所增加。澧水和沅水演替带在秋季和冬季都有增加的趋势,且增势较缓,而春季和夏季变化波动较大。在空间上,澧水演替带
浓度一直高于沅水演替带浓度,说明澧水演替带
浓度高于沅水演替带。
4.3. 磷酸盐与三氮浓度相关性
根据磷酸盐与三氮浓度关系,得到如图7所示相关性。从图中可以看出,磷酸盐与三氮相关性较大,且与
、
、
相关系数分别是0.8324、0.7288和0.7880。表明磷酸盐与三氮含量呈现

Figure 7. The correlation of
and
,
,
图7. 磷酸盐与三氮相关性
出正相关关系,即三氮浓度增加时,磷酸盐浓度也会增加。由于磷酸盐和三氮均是地下水中常见的污染物,它们经常相伴而生且循环过程是相互耦合的,因此磷酸盐与三氮浓度会在同一地点浓度较高,得出的研究结果与相关文献研究成果基本一致 [20] [21] [22] ,这也是造成湿地富营养化的主要原因。
4.4. 环境效应与治理建议
根据《地下水质量标准GB/T14848-93》,地下水中
浓度大于0.5 mg/L即划分为V类水。结合澧水和沅水演替带地下水质量监测结果可知,澧水演替带地下水中
浓度全年均大于0.5 mg/L,属于V类水,说明已经受到
的严重污染,不适用于饮用和灌溉。沅水一年中有8个月也都属于V类水。澧水演替带在2014年6月和2015年2月份超过III类可饮用水标准15倍,而5月更是超过III类可饮用水达28倍。说明澧水和沅水监测地段地下水受
污染已经达到了非常严重的程度,特别是澧水地下水受
污染最为严重。通过对监测结果的初步分析,认为湿地演替带环境不利于硝化反应的进行,促使
不断持续累积所致。
澧水演替带试验场地周围为农田区,施肥方式主要是撒施和灌水,溶解在地表水中的氮素也随水入渗进入到地下,经过较长时间入渗后最终进入地下水体中。另外,试验区不远处是陈家嘴镇农户集中居住区,生活污水大都未经处理直接就地排放到附近沟渠,沟渠也未采取任何防渗措施,经过一段时间后部分入渗到地下水中。澧水试验区地势平坦开阔,地形起伏不大,地下水水力坡度和流速都较小,这些条件都为氮磷在澧水地下水中的富集提供了有利条件。
沅水试验区,地形以丘陵平地为主,试验区域范围内无农田分布,主要为裸露地表的粘土层,夏季生长野草,冬天则裸露地表。试验区大范围内零星分布着一些住户和企业,生活污水和工业废水通过简单处理后直接排放到没有防渗措施的沟渠中,随后渗入到埋深较浅的地下水中,对地下水水质造成污染。该试验区地势相对平坦,地下水水力坡度和流速都较小,为氮磷在地下水富集提供了较有利条件。
由此可以看出,在湖泊地表水氮磷浓度超标,地表水和地下水通过相互作用会引发区域性地下水污染,影响地下水环境,危害人类饮用水安全,因此必须采取一定的措施来保证人类饮用水安全。
氮磷水环境污染治理十分棘手且成本过高,这是因为氮磷污染物不仅有天然来源还有人为来源,而人为来源又分为点源和面源,这都给治理带来了很大的困难。因此任何治理措施都要多管齐下、因地制宜。对天然污染源可以采取加强水体管理、加强湿地演替带建设、尝试生物治理和湖泊湿地淤泥清理等措施;对人为污染源可以采取施截污工程或引排污染源、建设污水处理厂、增加植被覆盖面积防止水土流失等措施。氮磷水环境治理是一项需要全社会共同承担的责任,是水资源持续安全地利用,社会可持续发展和生态建设的重要保障。
5. 结论
通过对洞庭湖区澧水和沅水湿地演替带氮磷分布特征及其环境效应的研究,可以得出以下主要结论:
1) 洞庭湖演替带地下水中不同形态氮、磷的空间分布均呈现出非均一性。澧水和沅水演替带地下水中
浓度年平均值分别为0.7526 mg/L和0.6395 mg/L,
浓度年平均值分别为0.0079 mg/L和0.0104 mg/L,
浓度年平均值分别为2.0337 mg/L和0.8059 mg/L。磷酸盐年浓度年平均值分别为0.4783 mg/L和0.3633 mg/L。以农业为主的澧水演替带中氮磷浓度高于非农业区的沅水演替带。
2) 不同形态氮、磷浓度在时间上的差异性比较明显。澧水演替带内,大量施肥引起地下水中NH4+-N浓度出现峰值,而
和
浓度也都是在2、3月浓度突然增加,是由于
在地下环境中发生了硝化反应,但略有迟滞现象。由于演替带环境不利于硝化反应的进行,两地都出现了NH4+-N高浓度污染。且在丰水期浓度差有加大的趋势。
3) N-P的相关性。水体中磷酸盐浓度与三氮浓度存在显著的线性正相关,且相关性较大,与
、
、
相关系数分别是0.8324、0.7288和0.7880。氮磷在水体中相伴而生,浓度共同增加是造成湿地富营养化的主要原因。
4) 氮磷浓度超标对环境造成一定程度的影响,尤其是在演替带,受到污染的地表水通过地表水和地下水的相互作用,对地下水环境造成污染,危害人类饮用水安全,值得引起重视。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(41272249)资助。