1. 引言
诺贝尔物理学奖得主理查德·费曼(R. P. Feynman)于1959年美国物理学会年会上提出了纳米科技的概念,揭开了人类向纳米科技进军的序幕。分子机器属于纳米科技范畴,由于具有许多独特的优异性能,因而在新材料、生物医药、储能系统以及传感器等领域具有广阔的应用前景。鉴于在分子机器研究方面作出了杰出贡献 [1] - [7] ,索维奇、斯图达特和费林加共同获得2016年的诺贝尔化学奖。
分子机器常用热能驱动,期间伴随热膨胀。研究分子机器构件的热膨胀性质,对于了解分子机器的热驱动机制,从而对于分子机器的正确设计和可靠应用,都是十分重要的,然而遗憾的是目前尚未见他人在这方面的实验及理论研究的报道。由于尺寸过于细小,目前对分子机器构件的热传导性质进行实验研究还存在较大困难,而只能在理论研究方面另辟蹊径。考虑到晶格动力学理论所具有的优势,我们曾用该理论研究过分子机器中环状分子这种常用构件的热膨胀性质,并得到了一些有意义的结果 [8] 。作为分子机器中另一种常用构件的链状分子,由于存在于环状分子中所没有的两端,因而有声波反射,这导致它们的热传导性质也不相同。因此本文将用晶格动力学方法对链状分子的热传导性质进行理论研究,并将链状分子与环状分子的热传导性质进行比较。
2. 链状分子的晶格动力学
设相邻距离为a、质量为m的相同原子构成无限长链状分子,相邻原子间线性力常数为β。热膨胀只与无限长链状分子中的纵波有关,原子l的纵向振动位移可表示为 [9]
(1)
其中,k为波矢,
为频率,
为振幅。频率与波矢间存在以下的色散关系:
(2)
设想在原子0和原子1以及原子N和原子N + 1之间解耦,即得包含N个原子的链状分子,其中只有驻波,因此该链状分子中的原子l的振动位移可表示为
(3)
根据链状分子两端符合的自由边界条件,得
(4)
(5)
其中,
对应于平动。
根据晶格动力学理论,得以下原子振动位移、动量和链状分子振动哈密顿公式 [9] :
(6)
(7)
(8)
其中,
和
为声子产生与消灭算符,
为声子数算符,平均声子数
符合玻色统计:
(9)
由(8)式和(9)式可知,当温度T处于绝对零度时,链状分子有零点振动,这是经典物理不能解释的量子效应,因此考虑了量子效应的晶格动力学相比于建立在牛顿力学基础之上的分子动力学更为准确,这是本文采用晶格动力学而不采用分子动力学的一个原因。
3. 链状分子的热膨胀
链状分子非和谐振动哈密顿可表示为
(10)
其中,
为p阶非和谐力常数,求和项就是p阶非和谐势能
。
设原子l和
的平衡位置坐标分别为
和
。我们根据微扰论曾得p阶非和谐势能
引起晶格常数热膨胀的公式 [10]
(11)
其中,
或
分别是由和谐晶体各种振动态的直积构成的未微扰态。
要使上式的求和项不为零,
和
状态则需相差一个声子,故
和
可分别表示为
(12)
(13)
将(10)、(12)和(13)式代入(11)式,得
(14)
当
,且
,即p为奇数时,由(14)式得
(15)
将(6)式代入上式,得
(16)
根据(16)式,可以求得整个原子链所有相邻原子间距热膨胀的平均值
,在此基础上求得原子链热膨胀系数γ。可见用晶格动力学理论,可以得到有关热膨胀性质的解析公式,便于分析其物理机制,而通过分子动力学,无法得到有关热膨胀性质的解析公式,这是本文采用晶格动力学而不采用分子动力学的另一个原因。
由于链状分子和环状分子具有不同的结构,计算中采用不同的边界条件,它们中存在不同的波动形式,链状分子中存在驻波,而环状分子中存在行波,它们的声子能谱也不相同,又由于热膨胀性质与原子振动有关,因此上面得到的链状分子原子间距热膨胀计算公式与文献 [8] 中得到的环状分子原子间距热膨胀计算公式明显不同,链状分子的热膨胀性质的计算结果肯定不同于环状分子的热膨胀性质的计算结果。
4. 数值计算结果与分析
虽然氩原子构成的链状构件在分子机器中没有具体应用,但由于氩原子间的相互作用能用L-J模型 [8] 准确描述,因此我们通过对它进行计算来了解链状分子的热膨胀性质的尺寸效应。不同长度(N分别为6和80)的链状分子的原子间距热膨胀平均值
和热膨胀系数γ在0-20K之间随温度t的变化分别如图1和图2所示,可知链状分子原子间距热膨胀平均值以及热膨胀系数都随温度增加而增加;短的链状分子的原子间距热膨胀平均值大于长的链状分子的原子间距热膨胀平均值,并且在低温情况下差异非常明显,而当温度升高时差异明显减弱;短链状分子的热膨胀系数小于长链状分子的热膨胀系数,同样在低温情况下差异也非常明显,而当温度升高时差异明显减弱。因此,低温下需要考虑链状分子热膨胀和热膨胀系数的尺寸效应,而在高温度下无需考虑。
设温度T为1 K,链状分子的原子间距热膨胀和热膨胀系数随长度的变化关系分别如图3和图4所示。由图3可知,当链状分子的长度较短时,随着链状分子的长度增加其原子间距热膨胀有显著减小;而当链状分子的长度较长时,随着其长度增加原子间距热膨胀平均值缓缓趋近于无限长链状分子的原子间距热膨胀平均值。由图4可知,当链状分子的长度较短时,随着链状分子的长度增加链状分子热膨胀系数有显著增加;而当链状分子的长度较长时,随着其长度增加热膨胀系数缓缓趋近于无限长链状分子的热膨胀系数。
为了与我们早先得到的环状分子的热膨胀性质的尺寸效应相比较 [8] ,图3和图4中还分别出示了环状分子的原子间距热膨胀以及热膨胀系数随长度变化的关系曲线,可知链状分子与环状分子具有完全不同的热膨胀性质的尺寸效应,这是由它们具有不同的结构、边界条件、振动模式及声子结构所导致的。
5. 结论
本文运用晶格动力学理论推导了链状分子的热膨胀及热膨胀系数公式,进行了数值计算,并根据计

Figure 1. Thermal expansion of interatomic spacing in chain molecule vs. temperature
图1. 链状分子中原子间距热膨胀与温度关系
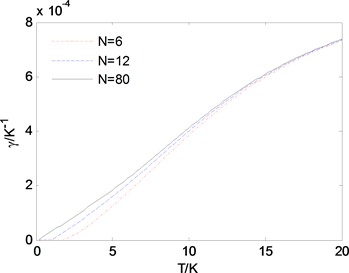
Figure 2. Thermal expansion coefficient of chain molecule vs. temperature
图2. 链状分子热膨胀系数与温度关系

Figure 3. Thermal expansion of interatomic spacing in chain molecule vs. its length
图3. 链状分子中原子间距的热膨胀与长度关系
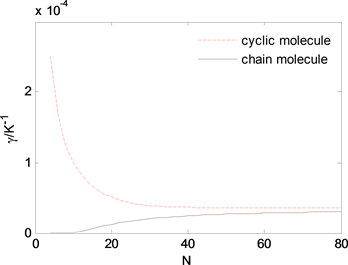
Figure 4. Thermal expansion coefficient of chain molecule vs. its length
图4. 链状分子热膨胀系数与分子长度关系
算结果分析了链状分子热膨胀性质的尺寸效应。研究结果表明,在低温下,链状分子热膨胀性质具有明显的尺寸效应:当链状分子较短时,随着其长度的增加原子间距热膨胀有显著减小,而热膨胀系数有显著增加;当链状分子较长时,随着长度的增加其原子间距热膨胀不再有显著减小,热膨胀系数也不再有显著增加,两者都缓缓趋于无限长链状分子的相应值。随着温度的升高,链状分子热膨胀性质的尺寸效应明显减弱直至消失。因此必须考虑在低温下的短链状分子的热膨胀性质的尺寸效应。研究结果还表明,链状分子具有与环状分子完全不同的热膨胀性质的尺寸效应。