1. 引言
De Finetti于1957年提出分红的概念,此后60年,风险理论中对于分红策略的研究一直是热门课题,先后出现了Barrier分红策略、Threshold分红策略 [1],后来学者们纷纷研究其最优性以及这两种策略的混合策略,随后,对Lévy过程研究的出现,为风险理论提供了新的思路 [2] [3] [4]。相较于经典风险模型,其对偶模型可以很好地刻画主要从事发明或勘探业务的公司盈余状况。近些年,随着精算学的发展,很多学者开始关注对偶模型中的分红问题 [5] [6] [7]。近几年Albrecher又提出了Ratchet分红策略 [8]。
2. 新混合策略简介
在Barrier策略中,要求在公司的盈余过程首次超过给定的参数b,那么多出的部分全部拿走用来做分红资金 [1],盈余过程继续随时间变化,若下一时刻的盈余水平未超过b,即没有出现新的峰值,则不分红;若出现了新的峰值,继续将新增部分全部拿走用来分红。而Ratchet分红策略的分红模式为:预先给定多个分红界,待公司拿初始资金进行无风险投资后,只要首次收益高于初始资金即将收益部分以固定分红率进行分红,继续以初始资金二次投资,待收益值再次高于投资值,观察收益水平是否突破某一分红界,突破则增加分红率,未突破仍以之前分红率进行分红,依此类推。这两种策略的分红模式启发我们想到,是否可以给Ratchet策略一个上界C,让Ratchet策略分红率的不断增长的情况提前结束,即分红率等于1,让收益值全部用来分红即可。下面对新分红模式展开具体分析。
3. 基础知识准备
首先,假定在完备带流概率空间
中,存在一谱正Lévy过程
,其中
。此过程的拉普拉斯指数可表示为:
其中,
其中
为漂移系数,
为扩散系数,
是在
上的有限测度且满足:
[9]。
其次,在此过程中定义分红策略
是由从0开始非降、右连续且
适应的过程。用
表示修正盈余过程,
,由于本文研究的分红策略是连续的,故
,且
时,
,其中
为安全负荷。下面定义分红策略
下的分红值函数:
。最后我们用
表示公司破产时刻,
[10]。
在Lévy过程波动理论中,尺度函数具有重要意义,下面我们给出过程
的第一类尺度函数
的定义:
其中
,
,
是右连续凸函数,
,
,
,
。过程S的第二类尺度函数
为:
, [9] [11].
基于2018年Albrecher提出的Ratchet策略 [1] 我们了解到:在盈余过程首次到达
水平之前(
),公司一直保持以固定的分红率
对股东进行持续分红,如果盈余过程达到了
水平,公司将立即增加分红率,以分红率为
进行分红,其中
,依此类推,根据前边介绍的新混合策略,待盈余水平超过了C,立即进行Barrier分红策略,将收益部分全部拿来股东分红。下面给出混合策略下盈余过程的随机微分方程:
其中
。混合策略下的分红值函数为:
其中,
此结果可参考文献 [6]。下面给出谱正Lévy过程首中时的定义以及相关结果。对于
,记
用
表示破产时刻。
引理3.1对任意
,我们有如下结论:
证明 此引理的证明可参考文献 [12] [13]。
4. 主要结果
定理4.1 对于
,谱正Lévy过程
先Ratchet后Barrier的混合策略的分红值函数为:
证明 首先我们考虑
的情形,此时盈余过程从开始到破产发生,将一直执行Barrier策略 [1],对高于C的部分全部拿来进行分红。分红值函数可表示为:
其次,对
情况,此时需要考虑盈余过程
是否可以达到C,谱正Lévy过程达到更高水平的方式有“爬”和“跳”两种,因此达到C水平时的状态是随机的。
对比谱负Lévy情况,我们做以下处理:
其中,
同理,
故
。
利用引理2.1的结果可知:
代入V(x)表达式可得结果。
最后,对
分析:这里的
相当于最初设置的界限,盈余过程超过此水平,就开始改变分红率,增加至
,未超出直接使用分红率
来分红。下面给出此部分的值函数解析式:
类似于上述方法,我们考虑:
其中,
,
可由上一种情况代入计算得到。类似上一种
情况使用引理2.1的结果代入可得表达式。
5. 图像分析
令
,得到定理4.1中尺度函数
图像以及定理的第二部分值
函数图像,分别见图1、图2所示:
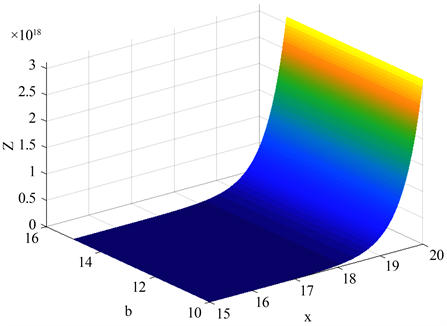
Figure 1. The q-scale function
图1. 尺度函数
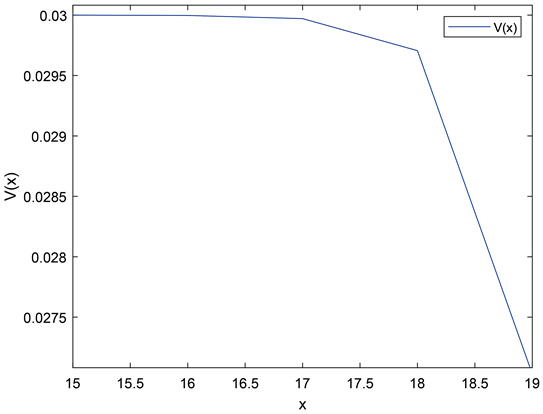
Figure 2. The value function
图2. 值函数