摘要: 昆明卷烟厂制丝线气流烘丝机烟丝出口含水率控制延迟长,滞后大,需操作人员频繁干预调整,烘丝出口含水率偏差大,并且明显高于集团对标值,同时与行业标杆企业比较存在一定差距。因此降低制丝线气流烘丝出口含水率偏差迫在眉睫。本文从制造精益、提升制丝产品内在质量方面着手、深入分析影响气流烘丝出口含水率的关键因素及烘丝机脱水控制原理。明确循环热风温度波动的主要症结,创造性地通过气流烘丝料头料尾分段控制和预估水分恒脱水自适应控制,实现气流烘丝出口含水率控制波动的减少,降低了出口含水率偏差。
Abstract:
Kunming Cigarette Factory silk wire air drying machine tobacco export moisture content control delay is long, lag is large, the operator needs frequent intervention adjustment, drying wire export moisture content deviation is large, and obviously higher than the group’s standard value, and there is a certain gap with the industry benchmark enterprises. Therefore, it is urgent to reduce the deviation of moisture content at the outlet of air drying silk. In this paper, the key factors affecting the moisture content at the outlet of air drying wire and the dehydration control principle of the drying machine are analyzed in depth from the aspects of making lean and improving the internal quality of the silk products. The main crux of temperature fluctuation of circulating hot air was identified, and the control fluctuation of water content at the outlet of air drying was reduced and the deviation of water content at the outlet was reduced through the creative control of the head and tail of air drying and the adaptive control of the predicted water constant dehydration.
1. 引言
目前气流烘丝出口含水率偏差是烟草行业对标评价的关键质量指标,同时也是行业各企业均在不断关注提升的关键工艺控制点。其稳定性是叶丝加工产品均质化的重要体现,同时影响着叶丝干燥后烟丝的物理、化学指标和成品烟丝卷制后的感光质量。因此气流烘丝出口含水率偏差控制是行业企业面临的关键性核心问题。烘丝出口含水率偏差是每批次根据相同时间点实际出口含水率和设定出口含水率之间差值的绝对值。采集计算固定数据量,并计算平均值,即为每批次烘丝出口含水率偏差。针对降低制丝线气流烘丝出口含水率偏差的控制方法,四川中烟工业有限责任公司成都卷烟厂提出了一种基于融合注意力时间卷积网络(Fused Attention Time Convolution Network, FATCN)的烘丝出口含水率控制方法。借助多元高斯分布检测和降噪自编码器对监测数据进行实时处理、特征衍生与增强,利用FATCN模型对监测数据进行实时判别,精准识别控制参数的调整时机和调整量,实现烘丝过程的自动化控制。有效地实现了降低制丝线气流烘丝出口含水率偏差的问题,但该方法控制方法复杂,成本较高 [1] [2] [3] [4] 。
2. 气流烘丝出口含水率波动原因分析
通过对关键控制点位制丝线气流烘丝出口含水率偏差不达标缺陷进行分类别统计,归纳出循环热风温度波动、入口含水率波动、入口电子秤流量波动、前段工序含水率波动、出口水分仪误检测等缺陷原因,统计不同关键控制点位不达标缺陷累计频次和累计百分比,统计数据如下表1。

Table 1. Statistical data on the cumulative frequency and cumulative percentage of non-compliance defects at critical control points
表1. 关键控制点位不达标缺陷数累计频次和累计百分比统计数据
由上表可知,循环热风温度波动引起出口含水率偏差不达标缺陷数为263,占合计数的74.93%。因此循环热风温度波动是主要症结。进一步分析影响循环热风温度波动的原因,绘制原因分析树图如下图1。
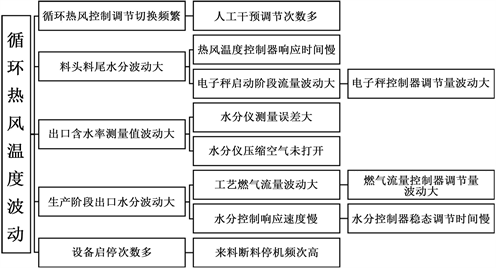
Figure 1. Analysis tree diagram of causes affecting temperature fluctuations of circulating hot air
图1. 影响循环热风温度波动的原因分析树状图
对影响循环热风温度波动的原因分析树状图上涉及的原因进行逐一确认,排除了人工干预调解次数多、电子秤启动阶段流量波动大、水分仪测量误差大、水分仪压缩空气未打开、工艺燃气流量波动大、水分控制响应速度慢、来料断料停机频次高等原因。
调查分析30个批次热风温度控制器响应时间对症结影响程度,热风温度控制器响应时间分组单因素方差分析,P值 < 0.05,即为显著性差异。
查阅生产制造系统,调查统计30批次生产过程热风温度控制器响应时间,确定生产过程热风温度控制器响应时间(s)范围在145 s~160 s之间(表2)。

Table 2. Hot air temperature controller response time grouping
表2. 热风温度控制器响应时间分组
为验证对症结影响程度,将热风温度控制器响应时间(s)分为145~150 s、151~155 s、156~160 s三组,在历史生产数据中,每组随机各抽样10批次循环热风温度波动系数CV (%)数据。

Table 3. Group circulation hot air temperature fluctuation coefficient CV (%) statistics
表3. 分组循环热风温度波动系数CV (%)统计
对上表3数据进行方差分析得出每组的方差P < 0.05在0.05水平存在显著差异,热风温度控制器响应时间(s)对循环热风温度波动有显著影响。确定热风温度控制器响应时间慢为的主要原因。
3. 制定对策
针对影响循环热风温度波动的原因制定相应的实施对策如下表4:

Table 4. Countermeasure implementation table
表4. 对策实施表
1) 对策实施一采用料头料尾和正常生产分段控制
a) 措施1构建料头料尾和正常生产分段控制切换流程
流程图如下图2:

Figure 2. Switching process between head and tail and normal production segment control
图2. 料头料尾和正常生产分段控制切换流程
b) 措施2确定料头料尾水分检测点
分别选取冷床后和烘丝出口振槽两处料头料尾水分检测点位,通过SET7仿真验证,并记录水分检测反馈时间。通过分析,冷床后水分检测点位反馈时间为1.5 s,烘丝出口振槽水分检测点位反馈时间为1 s,响应速度更快,因此选择烘丝出口振槽水分检测点为料头料尾控制水分检测点。
2) 对策实施二采用烘丝预估水分恒脱水自适应控制
a) 措施1优化水分控制系统架构。
系统架构如图3:
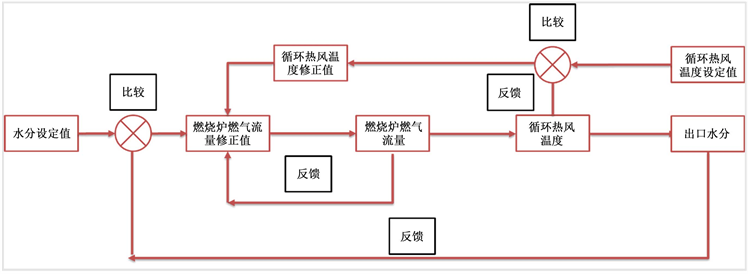
Figure 3. Optimized moisture control system architecture
图3. 优化水分控制系统架构
b) 措施2确定烘丝预估脱水量计算控制模型
根据控制器架构,大数据分析给定烘丝入口含水率设定值(%)SP(in)m、烘丝出口含水率设定值(%)SP(out)m、烘丝入口含水率瞬时值(%)PV(in)m、脱水量系数(0%~100%) K与脱水修正变量Temp 1和Temp 2的变化,寻找变量间关系。

Table 5. Analysis of calculation data for estimated dehydration amount of dried yarn
表5. 烘丝预估脱水量计算数据分析
根据表5分析,给定烘丝入口含水率设定值(%)SP(in)m、烘丝出口含水率设定值(%)SP(out)m、测量的烘丝入口含水率瞬时值(%)PV(in)m、脱水量系数(0%~100%) K与预估脱水修正变量Temp 1和Temp 2之间的关系为:
对策实施后,调查30批生产,观察分析气流烘丝机水分控制器稳态调节时间和设备正常生产阶段循环热风温度波动情况。

Table 6. Moisture controller steady-state adjustment time and circulating hot air temperature fluctuations
表6. 水分控制器稳态调节时间和循环热风温度波动情况
统计分析(表6)表明,水分控制器稳态调节时间 < 8 s,设备正常生产阶段循环热风温度波动系数CV (%) ≤ 0.2%,对策目标实现。
4. 结论
本文从制造精益、提升制丝产品内在质量方面着手、深入分析影响气流烘丝出口含水率的关键因素及烘丝机脱水控制原理。明确循环热风温度波动的主要症结,创造性的通过气流烘丝料头料尾分段控制和预估水分恒脱水自适应控制,实现气流烘丝出口含水率控制波动的减少,降低了出口含水率偏差。