1. 引言
丹江口水库是位于汉江流域中上游的一座综合性大型水利枢纽,是南水北调中线工程的水源地,也是治理开发汉江的关键性工程,具有防洪、供水、发电灌溉等多种功能。如何协调水库防洪安全与供水兴利之间的关系是管理者面临的一个重要任务。通过水文气象预测预报等先进技术,实施汛限运行水位动态控制和提前蓄水等措施,是目前提高水库洪水资源利用效率的主要非工程措施之一[1] 。
汛末提前蓄水的开始时间和蓄水方式的选择,是蓄水调度决策者最为关心的两个方面,同时也是水库蓄水策略研究的热点。现有的研究成果试图建立适应于所有来水情景下的蓄水调度规则、调度图或调度函数[2] ,没能利用蓄水开始前已有的水情信息,视来水情况灵活地制定提前蓄水方案。由于秋汛期是水库调度的关键时期,在确保防洪安全的前提下,还要尽可能地抓住时机蓄水,以保证枯水时期供水。因此,秋汛期的提前蓄水对水库的科学调度有着十分重要的意义[3] 。本文对丹江口水库的夏汛期与秋汛期洪水的相关性进行研究,利用Copula函数建立联合分布,分析夏汛期不同的来水情况下,秋汛期发生洪水的条件概率,为水库提前蓄水提供科学依据,在确保防洪安全的前提下,充分发挥水库的供水、发电等综合利用效益。
2. 基于联合分布的相关性分析
选择丹江口水库1954年~2011年的日流量系列和流域气象水文资料为实验数据,采用天气系统成因分析[4] 、数理统计分析[5] 、矢量统计和变点分析[6] 等方法,研究确定丹江口水库的汛期分期方式:将汛期划分为夏汛期(6.21~8.20)、过渡期(8.21~8.31)、秋汛期(9.1~10.10)三个分期,鉴于过渡期内仅在1956年8月23日、1993年8月27日、1976年8月28日发生了三场较小洪水,同时按照习惯且保证设计洪水取样,将丹江口水库的夏汛期与过渡期合并,将6月21日至8月31日作为夏汛期样本。分别统计夏汛期、秋汛期内最大洪峰流量,得到夏秋汛洪峰流量和夏秋汛最大7日洪量实测值,并进行相关性分析。
2.1. 零相关检验
衡量事物之间或变量之间线性相关程度的强弱,并用适当的统计指标表示出来,这个过程就是相关分析[7] 。一般,如果两个随机变量的线性相关系数越高,则相关系数的绝对值会越大;反之,则相关系数的绝对值越小。但是,有时即使两个随机变量的不相关,甚至相互独立,由于抽样的随机性仍有可能有较大的样本相关系数。因此常常有必要对相关系数是否为零进行检验,这种检验称为零相关检验[8] 。
将夏秋汛洪峰流量和夏秋汛最大7日洪量分别组成联合观测序列,采用Pearson方法计算相关系数r[9] 。采用零相关检验分析其相关性及相关程度。即提出原假设,H0:相关性为零;H1:相关性不为零。计算统计量rα的公式如下:
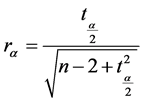 (1)
(1)
式中:n为样本数。取α = 0.1,查询t分布表得tα/2 = 1.672,代入式(1),算出rα = 0.218。若当统计量r的绝对值大于临界值rα时,则拒绝原假设,说明两个变量间相关性不为零;当统计量r的绝对值小于临界值rα时,则接受原假设,说明两个变量间相关性为零。
夏秋汛洪峰流量和夏秋汛最大7日洪量的Pearson相关性系数分别为0.37和0.40,均通过零相关检验,说明二者具有相关性,故选择其构建联合分布是合理的。
2.2. 边缘分布的确定
根据丹江口水库汛期分期结果,采用《水利水电工程设计洪水计算规范》[10] 方法,推求夏汛期和秋汛期的分期设计洪水。采用传统的矩法,计算不同分期各时段年最大序列的P-Ⅲ型分布参数,作为初始值,通过目估适线法确定参数,结果见表1。
2.3. 联合分布的建立
Copula函数是定义域为[0,1],均匀分布的多维联合分布函数[11] 。由Sklar定理,设 、
、 为连续的随机变量,边缘分布函数分别为
为连续的随机变量,边缘分布函数分别为 和
和 ,
, 为变量
为变量 和
和 的联合分布函数,则存在唯一的函数
的联合分布函数,则存在唯一的函数 使得:
使得:
 (2)
(2)
式中:u和v为随机变量的边缘分布函数;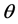 为Copula函数的参数,可由其与Kendall秩相关系数的关系求得。
为Copula函数的参数,可由其与Kendall秩相关系数的关系求得。
在水文分析计算中,常用的Copula函数有Gumbel-Hougaard、Clayton和Frank[12] 。为选择最合适的Copula函数,采用离差平方和最小准则(OLS)来评价Copula方法的有效性,并选取OLS最小的Copula作为联结函数[12] 。OLS的计算公式如下:

Table 1. The estimated parameters of P-Ⅲ distribution for summer and autumn flood peak and maximum 7-day flood volume
表1. 夏秋汛洪峰和最大7日洪量系列的P-III型分布参数估计值
 (3)
(3)
式中:n为样本数; ,
, 分别为经验频率和理论频率。
分别为经验频率和理论频率。
OLS的计算结果如表2所示,从表2可以看出,OLS值最小的Copula函数为Clayton函数,因此本文选取Clayton Copula作为联结函数。
计算夏秋汛洪峰和最大7日洪量联合观测值的经验分布值与理论分布值,点绘其经验分布值与理论分布值,得到图1(a)和图2(a),其线性相关系数分别为0.9954和0.9758,说明其经验分布和理论分布吻

Table 2. The optimized results of Copula functions
表2. Copula函数优选结果
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 1. (a) The correlation of empirical and theoretical distribution of peak floods; (b) The plots of empirical and theoretical distribution of peak floods
图1. (a) 洪峰经验分布与理论分布的相关图;(b) 洪峰经验分布与理论分布的拟合情况
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 2. (a) The correlation of empirical and theoretical distribution of maximum 7-day flood volume; (b) The plots of empirical and theoretical distribution of maximum 7-day flood volume
图2. (a) 最大7日洪量经验分布与理论分布的相关图;(b) 最大7日洪量经验分布与理论分布的拟合情况
合的很好。图1(b)和图2(b)以另外一种形式对联合观测变量的经验联合分布和理论联合分布进行了对比,图中的序号是根据联合观测值的理论分布进行升序排序后的序号。图1和图2表明,所建立的夏秋汛洪峰和最大7日洪量的联合分布是合理可行的。
采用Clayton Copula函数来构造夏汛期洪峰X和秋汛期洪峰Y的联合分布,夏汛期洪峰X和秋汛期洪峰Y的联合分布图如图3(a)所示,联合分布的等值线图如图3(b)所示。
采用Clayton Copula函数来构造夏汛期最大7日洪量X和秋汛期最大7日洪量Y的联合分布,夏汛期最大7日洪量X和秋汛期最大7日洪量Y的联合分布图如图4(a)所示,联合分的等值线图如图4(b)所示。
3. 条件概率分析
根据《水文情报预报规范》的相关规定[13] ,洪水量级的划分如下:1) 水文要素重现期小于5年的洪水,为小洪水;2) 水文要素重现期大于等于5年,小于20年的洪水,为中等洪水;3) 水文要素重现期为大于等于20年,小于50年的洪水,为大洪水;4) 水文要素重现期大于50年的洪水,为特大洪水。
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 3. (a) Joint distribution of peak floods during summer and autumn seasons; (b) Contours of peak floods during summer and autumn seasons
图3. (a) 夏秋汛期洪峰联合分布图;(b) 夏秋汛期洪峰联合分布等值线图
为了分析的方便起见,我们把特大洪水并入大洪水进行统计。
当已知夏汛期洪峰、最大7日洪量分别发生小水,中等洪水及大洪水,即当给定夏汛期洪峰、最大7日洪量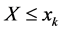 、
、 及
及 时秋汛期洪峰、最大7日洪量
时秋汛期洪峰、最大7日洪量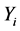 的条件概率分布分别为:
的条件概率分布分别为:
 (4)
(4)
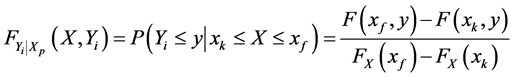 (5)
(5)
 (6)
(6)
得到秋汛期洪峰、最大7日洪量的条件概率分布图如图5所示,概率分布表如表3、4所示。
由表3可知,当夏汛期洪峰发生小洪水时,秋汛期洪峰发生小于五年一遇的洪水概率为82.1%,发生小于二十年一遇的洪水概率为95.6%,发生小于五十年一遇的洪水概率为98.2%,也即当夏汛期洪峰发
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 4. (a) Joint distribution of maximum 7-day flood volumes during summer and autumn seasons; (b) Contours of maximum 7-day flood volume during summer and autumn seasons
图4. (a) 夏秋汛期最大7日洪量联合分布图;(b) 夏秋汛期最大7日联合分布等值线图

Table 3. Conditional probability distribution of autumn peak flood
表3. 秋汛期洪峰的条件概率分布表
 (a)
(a) (b)
(b)
Figure 5. Conditional probability distribution of autumn flood peak when summer flood occur a specific magnitude, (a) flood peak; (b) maximum 7 days’ flood volume
图5. 夏汛期洪水发生特定量级洪水时秋汛期洪峰的条件概率分布,(a) 洪峰;(b) 最大7日洪量

Table 4. Conditional probability distribution of autumn maximum 7-day flood volume
表4. 秋汛期最大7日洪量的条件概率分布表
生小洪水时,秋汛期洪峰发生小洪水的概率较大,发生中等洪水和大洪水的概率很小。当夏汛期洪峰发生洪水的量级越大,秋汛期发生大洪水的概率越大。
由表4可知,当夏汛期最大7日洪量发生小洪水时,秋汛期最大7日洪量发生小于五年一遇的洪水概率为81.4%,发生小于二十年一遇的洪水概率为95.3%,发生小于五十年一遇的洪水概率为98.1%,也即当夏汛期最大7日洪量发生小洪水时,秋汛期最大7日洪量发生小洪水的概率较大,发生中等洪水和大洪水的概率很小。当夏汛期洪峰发生洪水的量级越大,秋汛期发生大洪水的概率越大。
4. 结论
本文分别对夏秋汛洪峰和最大7日洪量实测资料进行分析,并建立夏秋汛洪峰联合分布进行条件概率分析。由条件概率分析可知:当夏汛期洪峰发生小洪水时,秋汛期洪峰发生小于五年一遇的洪水概率为82.1%,发生小于二十年一遇的洪水概率为95.6%,发生小于五十年一遇的洪水概率为98.2%,也即当夏汛期洪峰发生小洪水时,秋汛期洪峰发生小洪水的概率较大,发生中等洪水和大洪水的概率很小。当夏汛期洪峰发生洪水的量级越大,秋汛期发生大洪水的概率越大;当夏汛期最大7日洪量发生小洪水时,秋汛期最大7日洪量发生小于五年一遇的洪水概率为81.4%,发生小于二十年一遇的洪水概率为95.3%,发生小于五十年一遇的洪水概率为98.1%。

NOTES
作者简介:胡瑶,女,硕士研究生,研究方向为水文统计。