摘要:
本文对尤溪河流域从点源、面源污染现状展开调查,通过污染负荷分析和估算方法对尤溪河流域水的污染源进行总体评价。研究结果表明:尤溪流域污染源以面源污染为主,点源污染所占比例极小。全流域各类污染源的污染物入河量中,畜禽养殖污染源和农闲污染源的COD、NH3-N的入河量比率最大,工业污染源的入河量是最小的;其中农田排放COD,新洋溪流域最大,占全流域总量的24%,其它支流依次为新桥溪、干流、源湖溪、青印溪、吉木溪、清溪。氨氮排放量,以青印溪排放量最大,占全流域总量的23%;另外生活污水排放,青印溪生活排放COD总量最大,占全流域总量的21%,其它依次为源湖溪、新桥溪、新洋溪、干流、清溪、吉木溪。总之全流域生活污水具有排污总量大、治理水平低的特点,生活污水对水体质量的危害程度十分明显。
Abstract: This paper investigates the Youxi River Basin from the point source pollution and non-point source pollution, and evaluates the source of pollution by analysis of the pollution load and esti- mation methods. The results show that the source of pollution of Youxi River Basin is mainly non- point source pollution, and a very small proportion of point source pollution. In all kinds of sources of pollutants into the river basin amount, livestock pollution and slack sources COD, NH3-N have the maximum ratio, and the river of industrial pollution is minimal; the farmland emission COD of the new Yangxi watershed is the maximum, 24% of the total accounted basin; other tributaries are Newbridge Creek, River, the source of Lake Creek, Green Indian Creek, Yoshiki Creek and the stream. Ammonia emissions of the Green Indian Creek is the largest, accounting for 23% of the total basin; for the additional sewage discharge, the largest COD emission is the Green Indian Creek, accounting for 21% of the total basin, followed by other sources: Lake Creek, Newbridge Creek, new Yangxi Creek, River, the stream and wood guitar Creek. In short, sewage basin has the characteristics of a large amount of sewage but low levels of governance; sewage degree of harm to the water quality is obvious.
1. 引言
河流由于其流动性,比较容易受到外来污染的影响,一旦局部发生污染,很容易波及整个流域,而且后果比较严重,会影响周围陆地的生态、河流地下水的生态、湖泊水库的生态以及下游河生态系统,因此河流的污染的危害远比湖泊水库等静态水体大。流域污染程度随径流量而变化。在排污量相同的情况下,河流径流量愈大,污染程度愈低;径流量的季节性变化,带来污染程度的时间上的差异。污染物扩散快。河流的流动性,使污染的影响范围不限于污染发生区,上游遭受污染会很快影响到下游,甚至一段河流的污染,可以波及整个河道的生态环境,污染危害大[1] 。河水是主要的饮用水源,污染物通过饮水可直接毒害人体,也可通过食物链和灌溉农田间接危及人身健康[2] 。近年来,我国多起重大污染事故均由流域水污染引起,水污染事故纠纷呈增加态势,河流断面水质污染严重,污染纠纷隐患重重,严重制约着我国经济与环境的协调发展[3] 。由于流域上下游之间存在经济利益的冲突,流域各地区根据自身的利益将会选择对自身有利的最优战略,使得各地区主要关注本地区范围内污染的治理,难以实现流域污染的有效治理[4] 。
本文采用排泄系数估算法来估算尤溪河流域污染负荷量以及分析集约化养殖污染负荷的空间分布规律。尤溪河流域污染主要是由工业点源、城镇生活污染和农业非点源污染造成的。点源污染主要是由工矿企废水排放和城镇生活污水排放而形成的,有集中的排污。由于工业行业、原料产品、生产工艺的多样性,通过工业废水进入尤溪的污染物不仅种类多而且数量大。因此,要对工业废水污染的排放量做出较准确的统计是比较困难的。
2. 研究材料和方法
研究以2011年《尤溪县统计年鉴》、《三明市统计年鉴》为基础数据,在GIS10支持下,数字化完成地图数字化录入、编辑和拼接,绘制成包括以县为单位的行政区划、水系、养殖场等数字地图,并建立属性数据库。根据实地调查,各地家畜的粪尿排泄系数有差异,综合其他参考文献[5] ,确定流域人和各类畜禽排粪、排尿系数及氮、磷含量[6] 。采用排泄系数估算法来分析尤溪流域不同地区集约化养殖粪便流失污染负荷(R)以及农田畜禽粪便负荷量(q) [7] 。本文采用的为第一次全国污染源普查方法[8] :
根据城镇生活源产排污系数核算体系的研究成果,结合第一次污染源普查数据库,城镇生活源水污染物核算由居民生活和第三产业两部分统一形成了以“城镇常住人口”为主要统计基量的污染物核算体系,其核算方法如下:
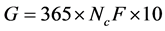 (1)
(1)
式中:
G——城镇生活源水污染物年产生量,单位:千克/年;
Nc——城镇常住人口,单位:万人;
F——城镇生活源水污染物产生系数,单位:克/人·天
根据工业污染源可根据该企业污染物产生量及所使用的末端治理技术计算系数(K),通过以下公式计算个污染物排放量:
污染物排放量 = 污染物产生量 ´ K (2)
K——为工业污染源排放系数,可查全国污染系数而得。
如果本区域畜禽在每个阶段的平均体重与参考体重不符,可以按照如下公式进行折算:
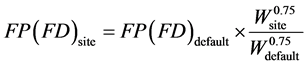 (3)
(3)
式中: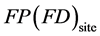 ——折算后的产污系数(排污系数),
——折算后的产污系数(排污系数),
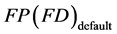 ——本手册系数表中查出的产污系数(排污系数),
——本手册系数表中查出的产污系数(排污系数),
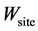 ——动物实际体重,kg,
——动物实际体重,kg,
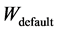 ——本手册给出的参考体重,kg。
——本手册给出的参考体重,kg。
3. 点源污染现状调查
在统计和计算尤溪流域工业污染负荷现状时,采用企业排污申报数据和环境保护部门的排污随视性监测数据,并辅以排污系数计算。根据尤溪县社会经济发展目标,工业污染物排放按照《三明市环境保护状况公报》(2011),其统计结果:尤溪流域废水直排入河的重点工业污染源有22家。22家重点工业污染源中直接排入
尤溪干流的有6家,直接排入新桥溪的有4家,直接排入青印溪的有2家,直接排入源湖溪的有10家。并且,根据调查显示,尤溪在产矿山有81家,如图1所示,矿山开采过程中,排放的污染物也对尤溪流域带来环境安全问题。重点工业污染源主要集中分布在尤溪河梅仙镇区、尤溪干流尤溪县城区和尤溪河上游段。2011年尤溪流域工业污染废水总计达5358万吨,其中重点工业污染源排放废水3645万吨,直接排入尤溪干流414.6万吨。排放COD 1135吨、NH3-N 326吨。工业废水排放量以尤溪河最多,为2749万吨,占排放总量的51.3%。COD排放量为349吨,占排放总量的30.7%。NH3-N排放总量为101吨,占排放总量的30%。尤溪河的铅锌重金属污染、梅仙的氰化物和铅污染以及尤溪流段内氯化物废石渣污染较为严重,给下游带来水环境安全隐患。从工业点源排放的行业性质来看,排放量主要集中在化工、造纸、电力、纺织和黑色冶炼等行业,这五个行业排放总量占全流域工业污水排放总量的68%,其中化工行业是全流域污水排放量最大的,占工业污水排放总量的57%,其次为黑色冶炼行业,占工业污水排
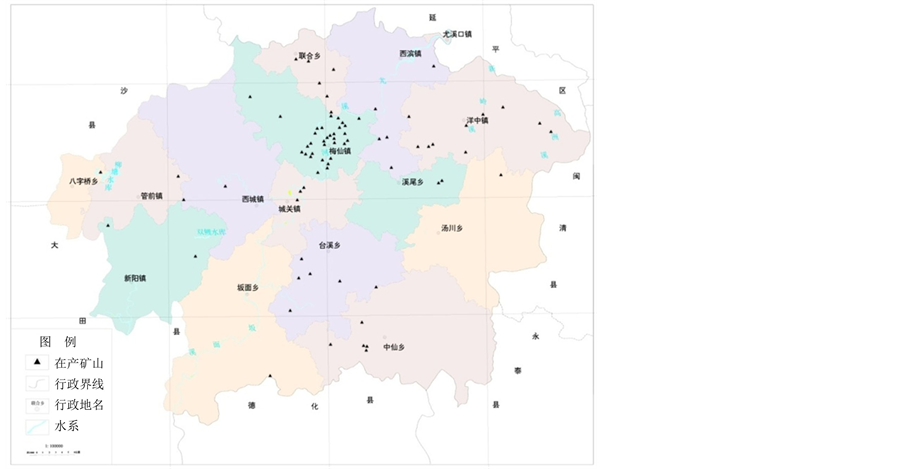
Figure 1. Youxi producing mines in distribution
图1. 尤溪在产矿山分布图
放总量的6.5%。全流域工业污水绝大部分排入尤溪水域且均没有进行处理,除梅仙段、西滨段、城关段若干重点工矿企业外,永定段重点工矿企业和其它小型企业均无排污许可证。目前全流域工业污水COD达标排放率均较低。
4. 非点源污染现状调查
非点源污染又称面源污染,是指无固定排放、污染物水源分敞的各种污染源的总称[9] 。通常面源主要包括农村生活污染来源、分散的畜牧养殖排污、农业生产过程施用的化肥和农药流失以及水土流失带来的污染物等。面源污染物在径流污染过程中占有相当大的比重,为了有效地防治和控制面源污染,需对其污染负荷进行计算。
4.1. 畜禽养殖污染负荷分析
长期以来,畜禽粪便一直作为农业生产的肥料返田使用。如粪肥供给养分超出当地农作物达到目标产量所需,势必造成作物施肥过量。一方面不利于作物的生长;另一方而,增加了非点源污染物的来源量,使周边水体受到严重的污染威胁。因此,有必要建立一个既考虑作物达到目标产量的需求,又尽可能地兼顾降低水环境受非点源污染风险的指标–耕地畜禽粪便最大负荷量,以便进行畜禽养殖环境风险评价和污染控制管理。国内外有关单位在畜禽动物污染源估算方面做了大量的工作,积累了许多数据资料,本文拟采用福建环境科学研究院的排泄系数法对畜禽养殖污染负荷进行估算。
1) 畜禽粪便污染物的排泄系数和污染物产生量估算
畜禽的粪便排泄系数是指单个动物每天排出粪便的数量,与动物的种类、品种、性别、生长期、喂养饲料甚至天气条件等诸多因素有关[10] 。根据三明市环境保护局推荐的估算系数,参照福建省环境科学研究院[6] 试验的畜禽粪便污染物排泄系数,并结合尤溪流域区畜牧饲养的实际情况,将尤溪流域地区的生猪生长一般为180 d,肉禽为60 d。
畜禽粪便污染为估算方便,将不同生长期、不同种类的禽畜,转换为已知排泄系数动物的相应量,进行畜禽粪尿产生量推算。根据全年畜禽饲养总量、畜禽粪尿及其污染物排泄系数得出本区畜禽粪便污染物的年产生量(表1)。可见,2011年畜禽全年产生的粪量为308.891万t,尿液213.48万t,粪尿合计达522.371万t,污染物BOD5为16.497万t,COD为20.699万t,NH3-N为1.541万t,TN为7.874万t,TP为0.973万t。污染物BOD5以尤溪干流、源湖溪、新桥溪较大。污染物COD以新桥溪、尤溪干流、青印溪、源湖溪较大。污染物NH3-N以源湖溪、新桥溪较大,TN以新桥溪、源湖溪、新洋溪较大。畜禽粪便一般通过两种途径进入水体:一是在饲养过程中直接排放进入水环境:二是在堆放储存过程因降雨和其他原因进入水体。研究表明,畜禽粪便的流失率为30%,2011年本区畜禽粪便污染物的流失污染负荷量为:粪尿量156.71万t,BOD5为4.95万t,COD为6.21万t,NH3-N为0.46万t,TN为2.36万t,TP为0.29万t。其中以新桥溪畜禽粪便污染物的流失污染负荷最大,为40.30万t。
2) 农田畜禽粪便负荷量分析
目前,流域畜禽粪便处理的主要出路是作为有机肥料直接还田,因此,统计流域畜禽粪便负荷量应以农田面积作为实际的负载面积[11] 。采用农田畜禽粪便负荷量这一量化指标可以间接衡量当地畜禽饲养密度及畜禽养殖业布局的合理性。鉴于各类畜禽粪便的肥效养分差异很大,统一换算成猪粪当量值加以分析。依据计算可得2011年各支流流域的畜禽粪便负荷量(见表2)。
在地域分布上,畜禽粪尿环境承载量较大的河流依次为:清溪、新桥溪、青印溪、吉木溪、源湖溪、新洋溪、尤溪干流,总体上尤溪流域上游长汀段承载量高于下游河段。从全流域来看,承载量大于3 t/亩的流域有5条,主要是新桥溪、清溪、青印溪、源湖溪、吉木溪;承载量大于4 t/亩的流域有有3条:新桥溪、清溪、青印溪、;承载量大于5 t/亩的流域有清溪。R指数反映了农田对畜禽粪尿的承受程度,随着R指数的增大,畜禽粪尿将逐渐超过农田承载能力,环境对畜禽粪尿的承受能力逐渐降低,对环境造成污染的威胁也随之越来越大,表3列出了农田对畜禽粪尿承受程度的警报值及其公级,级数越高表明畜禽粪尿对环境构成的污染威胁越大。过高的畜禽粪尿耕地承载量不仅无益于作物,而且会导致污染物从地表流入河水中,引起环境污染。
从目前流域畜禽粪尿承载量的实际情况分析,流域平均环境承载量警报值为0.92,已超过2级警报值,其中清溪警报值达到5级,新桥溪、、青印溪、新洋溪、尤溪干流、源湖溪警报值达到3级,吉木溪警报值达到2级。由此可以反映,尤溪流域畜禽粪尿承载量已较大程度地超过了农田环境的消化能力,新桥溪、清溪流域对环境已构成严重的污染威胁。
4.2. 其它非点源污染负荷分析
除了上述的工业废水污染及畜禽养殖业产生的污染外,农业灌溉、水土流失、城市径流等产生的污染物也是面源的来源之一。但这部分污染物目前还缺乏相对明确的估算方法,且在面源中占的比例也不大,难以考虑。根据《福建省流域综合规划修编》相关成果显示,农业污染物排放量按照定额计算,生活污水参照,人均COD、氨氦排放量分别为0.023kg/天·人、0.003 kg/天·人,计算各流域的COD和氨氮年负荷量,其估算结果如表4。
从表4中可以看出,2011年尤溪流域农田污染排放的COD总量为12546.4吨,氨氮为4018.2吨,其中新洋溪流域农田排放的COD总量为3012.7吨,占全流域总量的24%,其它支流依次为新桥溪、干流、源湖溪、青印溪、吉木溪、清溪。氨氮排放量中以青印溪排放量最大,为912.4吨,占全流域总量的23%,其它支流氨氮排放量依次为源湖溪、新洋溪、干流、新桥溪、吉木溪、清溪。2011年尤溪流域生活污水排放的COD总量为10365.9吨,氨氮为1389.4吨,其中青印溪生活排放COD总量最大,为2215.1吨,占全流域总量的21%,其它依次为源湖溪、新桥溪、新洋溪、干流、清溪、吉木溪。氨氮排放量中以青印溪排放量最大,为324.1吨,占流域总量的23%,其它依次为新桥溪、源湖溪、干流、新洋溪、清溪、吉木溪。全流域生活污水具有:排污总量大、治理水平低的特点,生活污水对水体质量的危害程

Table 1. 2011 Youxi Basin manure pollution production (unit: million tons)
表1. 2011年尤溪流域禽畜粪便污染生产量(单位:万吨)

Table 2. Youxi equivalent load of manure basin
表2. 尤溪流域畜禽粪便当量负荷量

Table 3. Farm animal urine bear on the extent of 4 t/acre alarm value
表3. 农田对畜禽尿承受程度的4 t/亩警报值
度愈发明显。据统计到2011年底止,尤溪流域5县城均没有城镇污水处理厂和生活垃圾无害化处理场,生活污水直排尤溪,对尤溪沿岸水质造成一定的影响。
5. 污染源总体评价
综上分析比较,尤溪流域水水环境状况和污染源分布状况(见图2),从点、面污染源的现状可以看出,污染物种类不同,其来源、负荷分配及地域特点都存在很大的差异性,尤溪流域污染源以面源污染为主,点源污染所占比例极小。主要污染程度严重区分布在梅仙镇和西滨镇范围,其他乡镇污染程度较轻。全

Table 4. Pollution and contamination of farmland life of Youxi River Basin
表4. 尤溪流域农田污染与生活污染情况
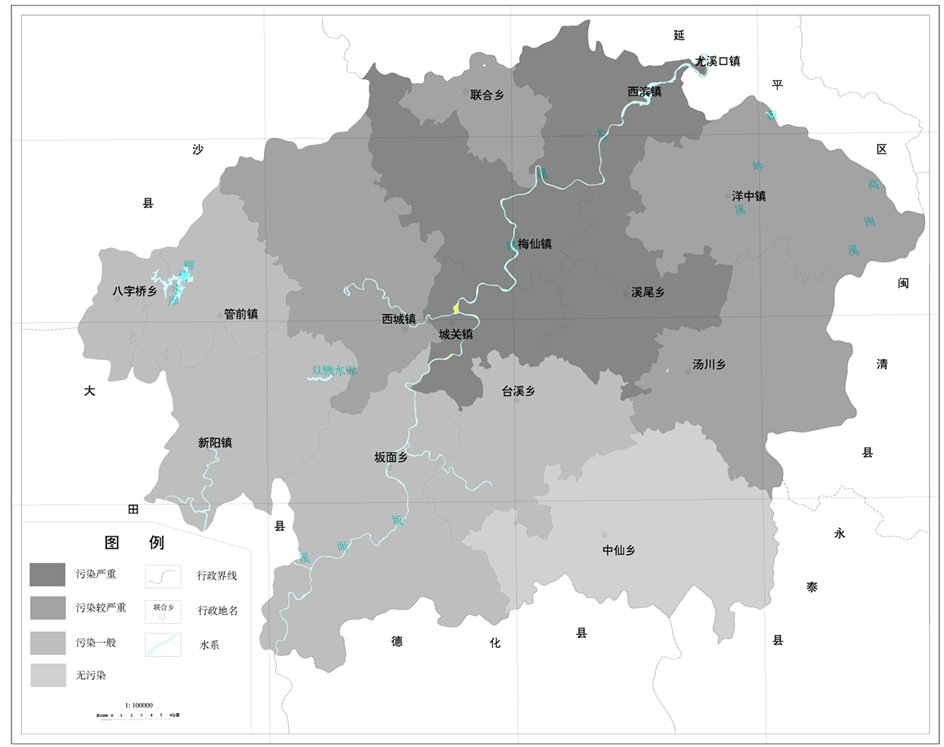
Figure 2. Youxi River pollution degree map
图2. 尤溪河流域污染程度图
流域各类污染源的污染物入河量中,畜禽养殖污染源和农闲污染源的COD、NH3-N的入河量比率最大,工业污染源的入河量是最小的。新洋溪流域农田排放的COD,占全流域总量的24%,其它支流依次为新桥溪、干流、源湖溪、青印溪、吉木溪、清溪。氨氮排放量中以青印溪排放量最大,占全流域总量的23%,生活污水排放,青印溪生活排放COD总量最大,占全流域总量的21%,其它依次为源湖溪、新桥溪、新洋溪、干流、清溪、吉木溪。氨氮排放量中以青印溪排放量最大,占流域总量的23%,其它依次为新桥溪、源湖溪、干流、新洋溪、清溪、吉木溪。全流域生活污水具有:排污总量大、治理水平低的特点,生活污水对水体质量的危害程度愈发明显。
基金项目
国土资源部公益性行业科研专项(201111020-2)。

NOTES
*通讯作者。