摘要:
用卡因菠萝1~2成熟,3~4成熟,5~6成熟,7~8成熟,9~10成熟和过熟6个不同成熟度的果实为材料,测定可溶性糖、维生素C、可滴定酸和可溶性固形物等指标,研究自然条件下,不同成熟度对菠萝果实品质的影响,确定最佳食用成熟度。结果表明,随着成熟度升高,四个品质指标含量总体均呈先增加后减少趋势。可溶性糖和维生素C含量都在7~8成熟时达到最高,分别为17.76%和178.11 mg/kg,且与其他各成熟度差异显著。可滴定酸可溶性固形物含量在5~6成熟时达到最高,分别为0.95%和16.87%,但与7~8成熟差异不显著。因此,卡因菠萝7~8成熟时食用可达最佳风味和营养品质。
Abstract:
Influence of 6 different maturity degrees on soluble sugar, vitamin C, titratable acid and total soluble solids content of “smooth cayenne” pineapple was studied to ascertain the best maturity degree for eating. The results showed that the quality properties increased firstly and then decreased with the increase of maturity degree. Contents of soluble sugar and vitamin C reached the maximum of 17.76% and 178.11 mg/kg at maturity grades 7 - 8, which were remarkable significantly higher than other maturity degrees. The titratable acid and total soluble solids content reached 0.95% and 16.87% at maturity grades 5 - 6, and they didn’t change remarkably at maturity grades 7 - 8. Assessed generally, maturity grades 7 - 8 are the optimum maturity with the best flavor and nutritional quality for eating.
1. 引言
随着我国经济的不断增长和人民生活水平的持续提高,追求生活的质量和品位已成为时尚和潮流。水果作为国民日常消费的一个重要组成部分,其品质越来越受到消费者重视。决定水果品质的因素众多,除品种、环境条件、栽培措施和养分管理水平等可以影响果实品质[1] -[6] ,成熟度高低也是影响果实品质的重要因素。研究表明,品种、成熟度对石榴总可溶性固形物、总糖、可滴定酸含量等品质指标均有重要影响[7] -[10] 。成熟度是能否保证商品果品质的关键因子之一,成熟度不足,果实发育不良,糖分积累不足,色泽差,缺乏应有的风味;果实过分成熟,则果肉松软,风味变差,货架期短[11] [12] 。因此,研究成熟度对果实风味和品质的影响,为消费者食用水果提供参考具有重要意义。果实一般有后熟过程,什么成熟度食用营养、健康、科学,是消费者普遍关心的问题,也是消费者在一定程度上可以选择的过程。菠萝是世界上重要的水果之一,研究菠萝的最佳食用成熟度对保持果实风味,避免果实品质下降等具有重要意义,有关不同成熟度的果实品质差异还鲜有研究。试验以卡因菠萝(Smooth Cayenne)为材料,研究自然成熟菠萝果实品质随成熟度的变化规律,为研究果品品质和确定最佳食用成熟度提供理论依据和参考。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. 试验材料
试验材料为卡因菠萝6个不同成熟度果实:1~2成熟、3~4成熟、5~6成熟、7~8成熟、9~10成熟和过熟。于2013年4月采自南亚热带作物研究所植物营养试验基地(表1)。
2.2. 试验方法
分别采集6个成熟度果实各6个,于实验室测定品质指标。可溶性糖含量用蒽酮比色法测定[13] ,维生素C含量用2,6-二氯靛酚法测定[14] ,可滴定酸含量用酸碱中和滴定法(以柠檬酸计)测定[15] 。
2.3. 数据统计
试验数据采用Excel 2007和SAS 8.0软件进行分析,Duncan’s多重比较检验处理间的差异显著性。
3. 结果与分析
3.1. 不同成熟度对菠萝可溶性糖含量的影响
由图1可以看出,菠萝可溶性糖含量与成熟度关系密切,在果实自然成熟过程中,随着成熟度的升高,可溶性糖含量增加,5~6成熟至7~8成熟时增加明显,7~8成熟时达到最高,为17.76%,显著高于其他成熟度。之后大幅下降,9~10成熟时可溶性糖含量相比7~8成熟时下降16.22%。
3.2. 不同成熟度对菠萝果实维生素C含量的影响
由图2可以看出,不同成熟度菠萝果实的维生素C含量总体呈先增加后减少趋势,降幅最大的是9~10成果实。7~8成熟时维生素C含量达到最高,为178.11 mg/kg,显著高于其他成熟度,之后下降较快。
3.3. 不同成熟度对菠萝果实可滴定酸含量的影响
由图3可以看出,在菠萝果实由绿熟转为黄熟的过程中,可滴定酸含量总体变化趋势也是先增加后减少,9~10成熟时含量最低,过熟果实含量又有所回升。5~6成熟时可滴定酸含量达到最高,为0.95%,但与7~8成熟时差异不显著。
3.4. 不同成熟度对菠萝果实可溶性固形物含量的影响
由图4可以看出,在菠萝自然成熟过程中,可溶性固形物含量总体也呈先增加后减少趋势。菠萝果实可溶性固形物含量在1~2成熟时最低,为13.97%,5~6成熟时最高,为16.87%,比7~s8成熟高出1.30%,但差异不显著。

Table 1. Evaluation standards of pineapple maturity degrees
表1. 菠萝果实成熟度评定标准

Figure 1. Soluble sugar content of pineapple fruit at different maturity degrees
图1. 不同成熟度果实可溶性糖含量变化情况
3.5. 不同成熟度对菠萝果实植物学性状和品质性状的影响
菠萝果实在成熟度不足时,果肉颜色、香味较淡,口感较差,商品性不好。成熟度过高,果肉色泽变暗,有稍许酒味,且容易腐烂,商品性差。在7~8成熟时,色、香、味俱全,具有最佳的品质和风味,与5~6成熟差异不显著(表2)。
4. 结论与讨论
适宜的采收成熟度是维持果实商品性的重要保证,成熟度的增加可以加速组织的衰老进程[16] 。菠萝属非跃变型果实,其后熟软化是一个渐变的过程。在菠萝果实自然成熟过程中,即从绿熟、黄熟、完熟到过熟,可溶性糖和Vc含量呈先上升后下降趋势,7~8成熟时各指标含量达到最高,分别为17.76%和178.11 mg/kg,且与其他各成熟度处理差异显著。石榴的研究也有类似的结果,在石榴成熟过程中,总糖含量呈显著上升趋势,于开花期结束后140天(相当于本试验中的7~8成熟)采摘的石榴果实,糖酸比最高[17] 。本试验中,可滴定酸含量在5~6成熟时达到最高,为0.91%,但与7~8成熟差异不显著,9~10成熟时最低。葡萄的研究也有类似的结果,5~6成熟时葡萄的酸含量为0.97%,达到7~8成熟和9~10成熟时,逐渐降低[18] 。另外,本研究中,菠萝可滴定酸呈先升后降趋势,而石榴和枇杷在果实由未熟、半熟到完熟的过程中,可滴定酸含量一直呈下降趋势[17] [19] ,原因可能和菠萝果实含水量较高有关。在果

Figure 2. Vitamin C content of pineapple fruit at different maturity degrees
图2. 不同成熟度菠萝维生素C含量变化情况
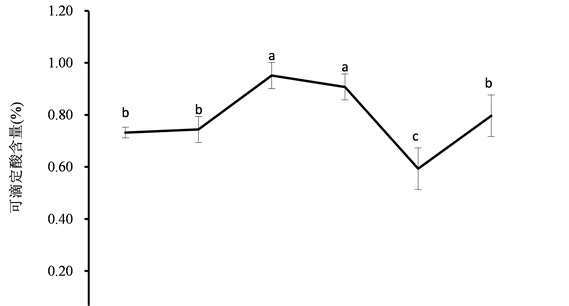
Figure 3. Titratable acid content of pineapple fruit at different maturity degrees
图3. 不同成熟度菠萝可滴定酸含量变化情况
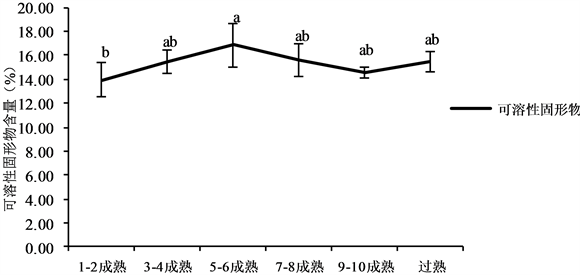
Figure 4. Total soluble solids content of pineapple fruit at different maturity degrees
图4. 不同成熟度菠萝可溶性固形物含量变化情况

Table 2. Botany properties and quality characters of pineapple fruit at different maturity degrees
表2. 不同成熟度菠萝果实植物学性状和品质性状变化情况
实达到7~8成熟时,可溶性糖、Vc、可滴定酸和可溶性固形物含量分别比过熟处理高22.82%、84.63%、13.75%和0.10%。成熟度过高,各指标含量大幅下降,风味变差,色泽发暗,且容易腐烂,商品性差。成熟度不足,不仅影响果品的产量和品质,而且风味严重淡化,影响商品价值[20] 。在选择菠萝时不能选择过生或过熟的果实,尤其不能选择过熟水果。对于消费者而言,根据外观色泽,选择7~8成熟的菠萝是明智选择,可立即食用,不仅色、香、味俱全,而且营养价值较高。如需贮存几天,建议选择5~6成熟果实。
因此,为了达到最佳的风味和营养品质,卡因菠萝果实应在7~8成熟时食用。菠萝品种、采收时间,也可能影响成熟度。消费者在具体实务操作时,应根据实际情况灵活掌握。
基金项目
国家科技支撑计划项目(2014BAD16B06),中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项(1630062014020;1630062014014),作物物种资源保护与利用项目(2014NWB047)。

NOTES
*通讯作者。