1. 引言
随着电力电子技术的发展,PWM并网逆变器的应用前景日益广阔。为此,各种各样的波形控制技术层出不穷。
目前,先进的控制算法越来越多的引用到逆变器的控制中来,高速数字信号处理器的发展为其提供了可能性。在控制方法上,随着各种高速数字信号处理器以及离散控制方法的出现,将先进的控制算法应用到并网逆变器控制中的研究越来越多。
应用较多的先进控制算法有PI控制、PID控制、双环控制、滞环控制、空间矢量控制、重复控制理论、状态反馈控制、无差拍控制、滑模变结构控制、智能控制、自适应控制等。这些控制算法的引入使逆变器输出的电能质量和转换效率大大提高。每种控制算法都有自己的特点,在独立控制逆变器时存在各自的优点与不足之处[1] -[4] 。
2. PWM逆变器主要控制策略及其优缺点
2.1. 并网逆变器的PI控制
PI控制形式简单,易于设计,鲁棒性强,理论成熟,是当前应用最广泛的控制方式,由于空载的PWM逆变器近似于一个临界振荡环节,积分(I)控制又增加了相位滞后,这样一来,为保证系统稳定,对比例(P)控制器必须有所限制。因此PI控制的快速性虽相对于均值反馈有较大改善,但仍是有限的,系统对非线性负载扰动的抑制效果不佳。实际上,由于单纯PI控制无法实现对正弦指令的无静差跟踪,往往需要增加外环均值反馈以保证系统的稳态精度[5] -[7] 。
2.2. 并网逆变器的PID控制
早期逆变器的波形控制通常采用模拟PID控制,单纯采用输出电压的瞬时值反馈,利用模拟PID控制器进行调节。PID控制算法简单、鲁棒性好、可靠性高、参数易于整定。PID控制是将偏差的比例、积分和微分通过线性组合构成控制量,对被控对象进行控制。控制偏差量由给定值与实际输出量构成。PID控制算法包括了动态过程中过去、现在和将来的信息:比例环节蕴含了动态控制过程中现在的主要信息,能够校正偏差;积分环节代表了过去积累的信息,能消除静差,改善系统的静态特性;微分环节代表了将来的主要信息,可超前控制信号变化,在过程开始时强迫过程加速进行,过程结束时减小超调,克服振荡,提高系统的稳定性,加快系统的过渡过程。逆变器采用模拟PID控制时,如果只是输出滤波电感或输出滤波电容的电流瞬时值引入反馈,其性能将得到较大改进。然而,庞大的模拟控制电路使得控制系统地可靠性下降、调试复杂、不易于整定、PID控制无法实现对正弦指令的无静差跟踪,实际上往往需要增设外环均值反馈以保证系统的稳态精度。但随着DSP的出现,逆变器的瞬时值反馈数字PID控制成为可能。数字信号处理芯片的出现使得这个问题迅速得以解决,如今各种补偿措施及控制方式可以很方便地应用于逆变电源的数字PID控制中,控制器参数修改方便,调试简单。但是,数字PID控制算法应用到逆变电源的控制中,不可避免的产生了一些局限性:一方面,系统的采样量化误差降低了算法的分辨率,使得PID调节器的精度变差;另一方面,采样和计算延时使得被控系统成为一个具有纯时间滞后系统,造成PID控制器的设计困难,稳定性减小[1] [3] 。文献[8] 提出了一种预测型PID控制器,较好地克服了时间滞后造成的影响。如图1所示。
2.3. 并网逆变器的双环控制
双环控制是在逆变器中普遍使用的一种方式,它兼备良好的动静态性能。这种控制方法是在电压环内增加一个电流内环,通过这种方式能显著提高系统的动态响应速度,及时的削减负载扰动造成的影响。同时,由于电流内环改善了被控对象,可以大大简化电压外环的设计。它的缺点主要是电流内环为抑制非线性负载扰动,必须具有足够高的带宽,才能获得满意的性能,这加大了数字控制器实现的难度[9] [10] 。如图2所示。
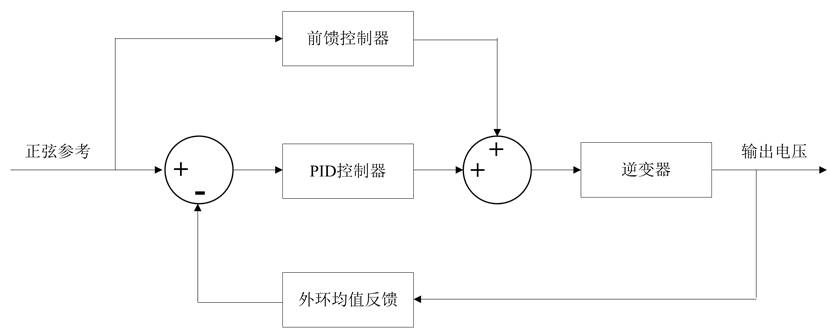
Figure 1. Control block diagram of PID control system
图1. PID控制框图
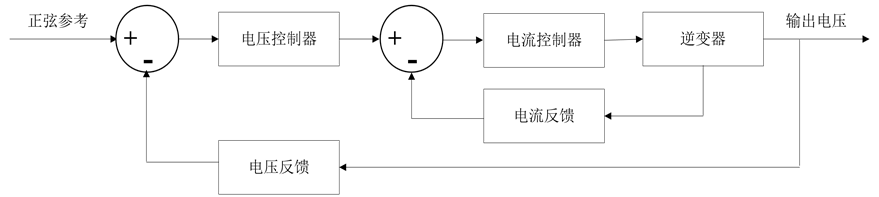
Figure 2. Control block diagram of dual-loop control system
图2. 双环控制框图
2.4. 并网逆变器的滞环电流控制
滞环电流控制是通过电流偏差来控制开关管开通或者关断的一种技术。把待控制的电流与基准电流的偏差量送入滞环比较器,当偏差量达到设定值时,改变开关状态。这种控制方法优点是简单、谐波小、动态性能好、对负载参数变化不敏感,其缺点在于开关频率并不稳定,它随着电流的波动而不断变化,给交流滤波器的设计增加了难度,也增加了开关管的损耗及应力[1] 。如图3所示。
2.5. 并网逆变器的重复控制
重复控制是消除各种周期性扰动最有效的方法之一,是在控制系统内部植入一个数学模型,来消除非线性扰动的控制方法。在一个并网逆变器中,由于给定的基准和输出的量都是正弦量,所以误差信号是周期变化量。根据内模原理:若要求一个反馈控制系统具有良好的跟踪指令以及抵消扰动影响的能力,并且这种对误差的调节过程结构式稳定的,则在反馈控制环路内部必须包含一个描述外部输入信号指令和扰动信号动力学特性的数学模型,以构成高精度反馈控制系统,该数学模型就是所谓的“内模(internal model)”。所以我们在闭环控制系统中增加一个周期的激励信号来抵消误差的周期性变化。其控制思想是假定前一周期出现的输出电压波形畸变将在下一周期的同一时刻再次出现,控制器根据参考信号和输出电压反馈信号的误差来确定所需的校正信号,然后,在下一个基波周期将此信号叠加在原控制信号上,这样就可以消除输出电压的周期性畸变。因此,重复控制的优点在于能很好的消除非线性负载及其他周期性干扰引起的波形畸变并且具有极佳的稳态性能。但由于延迟因子的存在,重复控制得到的控制指令并不是立即输出,而是滞后一个参考周期后才输出,这样,如果系统内部出现干扰,消除干扰对输出的影响至少需要一个参考周期,干扰出现后的一个参考周期内,系统对于干扰不产生任何调节作用,这一个周期系统近似处于开环状态,因此重复控制系统缺点表现为其动态响应较差,故重复控制一般和其他PWM控制方式相结合,用来改善输出电压波形[1] [3] 。有较多文献提出了鲁棒重复控制[11] [12] 、自适应重复控制[13] [14] 、伺服控制器、状态反馈控制与重复控制组成的双环控制等多种方案改善系统的动态性能。如图4所示。
2.6. 并网逆变器的无差拍控制
无差拍控制是一种基于微处理器实现的PWM方案。它根据逆变电源系统的状态方程和输出反馈信号来计算逆变器的下一个采样周期的脉冲宽度。此算法中,每个采样间隔发出的控制量是根据当前时刻的状态向量和下一个采样时刻的参考正弦值计算出来的,由负载扰动或非线性负载引起的输出电压偏差可在一个采样周期内得到修正。无差拍控制的优点是有极高的动态性能,输出能够很好地跟踪给定值。其缺点在于对系统参数反应灵敏,系统鲁棒性不强,瞬态超调量较大,当负载变化,非线性负载或者温度、运行条件等原因出现参数波动,都容易造成系统的不稳定或者输出性能恶化。另外,由于采样和计
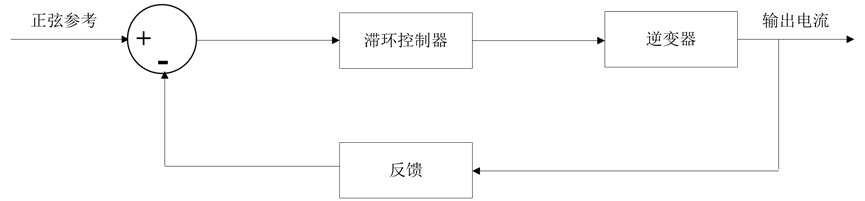
Figure 3. Control block diagram of hysteresis control system
图3. 滞环控制框图
算时间的延时,输出脉冲的占空比受到很大的限制[15] -[18] 。如图5所示。
2.7. 并网逆变器的状态反馈控制
状态反馈控制利用状态反馈,即将逆变器中的状态变量通过适当的系数反馈,可以合理地配置系统的极点,改变系统的阻尼比,提高系统的动态特性。从控制理论的角度来说,闭环系统性能与闭环极点密切相关。经典控制理论用调整开环增益及引入串、并联校正装置来配置闭环极点来改善系统性能;而在状态空间的分析中,除了利用输出反馈外,主要利用状态反馈来配置极点,它能提供更多的校正信息,从而得到最优的控制规律,抑制或消除扰动的影响。与双闭环控制类似,状态反馈波形控制系统也需要两个反馈变量,但是并不用它来构成独立的闭环控制回路,而是在状态空间概念上通过合理选择反馈增益阵来改变对象的动力学特性,以实现不同的控制效果。状态反馈的优点是可以大大改善系统的动态品质,因为它可以任意配置闭环系统的极点。但由于建立逆变器状态模型时很难将负载特性完全考虑在内,所以状态反馈缺点在于其控制只能针对空载或假定阻性负载进行,如果不采取相应措施(增设负载电流前馈补偿,预先进行鲁棒分析等),则负载的变化将导致稳态偏差的出现和动态特性的改变。文献中往往将状态反馈作为内环、以其它的控制策略作为外环形成复合控制方案[19] [20] 。
2.8. 并网逆变器的滑模变结构控制
滑模变结构控制是利用某种不连续的开关控制策略来强迫系统的状态变量沿着相平面中某一预先设计好的“滑动模态”轨迹运动,从而达到预期的性能。早期的滑模变结构多采用模拟控制技术,这存在着控制硬件电路复杂、控制功能有限的弱点,严重阻碍了它的发展,然而用微处理器通过软件可以比较方便的实现滑模变结构控制。离散滑模变结构控制包括两个部分:前馈控制和滑模控制。前馈控制保证
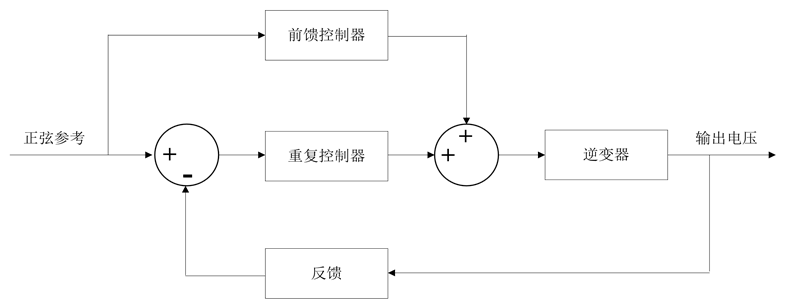
Figure 4. Control block diagram of repetitive control system
图4. 重复控制框图

Figure 5. Control block diagram of deadbeat control system
图5. 无差拍控制框图
系统输出电压有较好的跟踪质量,滑模控制不是连续控制,而是一种开关控制,它使系统运行于换一种滑动模态,保证系统较强的鲁棒性。选取适当的状态变量,利用状态空间法可求出滑模控制。滑模变结构控制系统的优点是其对参数变化和外部扰动不敏感,具有强鲁棒性,而且其固有的开关特性吸引了众多学者将它应用于逆变电源的控制之中。滑模变结构控制系统的缺点在于,其存在着系统稳态效果不佳、理想滑模切换面难于选取、控制效果受采样率的影响、会出现系统抖振的问题等不足。数字滑模变结构控制只有当采样频率足够高时才能实现较好的性能,这些都限制了它的应用。另外,就波形跟踪质量来说,滑模控制又不及重复控制和无差拍控制[21] 。
2.9. 并网逆变器的智能控制
智能控制主要包括神经网络控制和模糊控制等。模糊控制,是模仿人的思维方式,对难以建立精确数学模型的对象实施的一种控制策略,它是模糊数学同控制理论相结合的产物。复杂的电力电子装置是一个多变量、非线性、时变的系统,系统的复杂性和模型的精确性总是存在着矛盾。而模糊控制能够在准确和简明之间去的平衡,有效地对复杂事物做出判断和处理。智能控制的主要优势在于它不依赖于精确的数学模型,是模仿人的智能。模糊控制的优点表现为抗干扰能力强,响应速度快,有较强的鲁棒性,查找模糊控制表只需要占用处理器很少的时间,并可以任意精度逼近任何非线性函数。模糊控制的缺点则在于其中的知识表,模糊规则是基于专家经验,带有一定的人为因素,模糊变量的分档和模糊规则数都受当前技术水平的限制,因此需要进一步研究和完善。神经网络控制是从人体工程学出发,模仿人的细胞处理信息的过程。这两种方法的使用是建立在模型比较难以建立的基础上。对于模型容易建立的系统,可用现有的比较成熟的控制方式[22] -[24] 。
2.10. 并网逆变器的自适应控制
自适应控制与常规的反馈控制相比,自适应控制依据模型和扰动的先验知识比较少,需要在系统的运行过程中不断提取模型的信息,使模型逐步完善。主要有两大类:模型参考自适应系统和自校正控制系统。自适应控制系统是利用一个生成所期待的响应的模型作为参考模型并将其包括在控制策略中,利用实际系统与参考模型响应间的误差来修正控制器参数,以便使实际系统的响应收敛于所期待的的响应;自校正控制的基本思想是将参数估计递推算法与各种不同类型的控制算法结合起来,形成一个能自动校正控制其参数的实时的计算机控制系统。目前,自适应控制在电力电子领域应用得还不深入,由于它对过程参数的变化和未建模部分的动态过程不敏感、对动态过程变化的自适应性等特点,将会越来越多地应用于电力电子系统控制中[25] 。
3. 并网逆变器单一控制策略对比
目前的一些主要并网逆变器单一控制策略的优缺点比较如表1所示。
4. 并网逆变器的复合控制策略
并网逆变器的各种单一控制策略各有所长,在某些方面存在一些问题。因此,可以将不同方法整合成复合控制,以达到理想的控制效果。
文献[26] 讨论了双闭环PI控制和PI+重复控制在死区时间、非线性负载和电网电压扰动下的控制效果。通过仿真对比验证了PI+重复控制的复合控制策略能够很好的抑制周期性扰动和非线性负载引起的波形畸变,能够进一步提高电能质量。文献[27] 和文献[28] 通过对并网逆变器分别进行的PI控制、重复控制、PI与重复控制的仿真实验得出结论:仅有PI控制时,系统输出电压畸变较大,但系统输出波动较小。仅有重复控制时,系统稳态输出波形质量好,但系统负载突变时输出电压波动很大。采用基于重复

Table 1. Contrast of the control strategy for grid-connect inverter
表1. 常用并网逆变器的控制策略对比
控制和PI的复合控制方案后,系统得到了较满意的稳态输出波形和动态结果。文献[4] 研究了PI控制和重复控制互为补偿的复合控制技术。PI控制器和重复控制器并联在控制系统的前向通道中,取长补短,共同对系统的输出产生影响:当系统稳态运行时,重复控制器占主导作用;当负载出现大扰动、跟踪误差突然变大时,PI控制器决定扰动后第一个周期的系统输出,而后二者相互协调,使系统达到稳态。重复控制器用来消除系统的周期性跟踪误差,改善系统的稳态补偿精度;PI控制对输出谐波指令误差进行实时调整,提高系统的动态特性使系统具有良好的稳态和动态特性。文献[29] 研究了基于PI控制和改进的重复控制相结合的新型复合控制策略,仿真表明新的控制策略能有效改善并网电流波形,基本实现并网电流无差跟踪,同时保证并网逆变器输出电流与电网电压同频同相。文献[30] 提出了一种基于旋转坐标变换得PI控制,电压前馈补偿和重复控制相结合的复合控制方案。并通过仿真和实验证明该方案既能向电网输送功率因数接近1的有功电流,又能向电网发送无功,对电网进行无功补偿。不仅保证了微网并网的系统输出,而且提高了电能质量。
文献[31] 通过控制系统仿真,验证了采用PID控制和重复控制相结合的复合控制策略,对输出波形畸变的改善作用。而被控逆变系统具有多变量、非线性、参数时变性以及模型不确定的情况,辨识整定方法不一定有效,故而文献[31] 又提出了基于模糊PID控制和重复控制的逆变系统波形复合控制策略。它将模糊控制理论应用于逆变系统控制,证明了系统从空载到突加负载时,该复合控制策略下输出波形光滑,能很好的跟踪参考正弦电压,系统响应速度快。文献[32] 提出了一种基于对角递归神经网络在线辨识自学习整定PID控制和重复控制相结合的复合控制策略,递归神经网络只需较少的神经元和权值,适用于处理时变的输入、输出过程,具有较好的处理动态问题的能力。神经网络在线识别自学习整定控制器和重复控制器并联在一起,共同影响系统的输出,保证系统输出波形有良好的误差跟踪能力,又具有快速的动态响应性能。文献[33] 提出了一种神经网络内模控制和PID控制相结合的复合波形控制策略。建立了3层BP神经网络内部模型,并将其作为三相逆变器的内部模型,预测实际输出,采用PID控制器在线修正、补偿内部模型与三相逆变器之间的模型失配。当系统接阻性负载或整流性负载时,该控制方法所得的稳态电压误差和输出电压的谐波畸变率均小于其他控制方法。
文献[34] 针对光伏电池非线性强的特点,采用模糊控制和双闭环控制的复合控制策略。将模糊控制方法应用到光伏系统的MPPT控制,实现系统快速响应外部环境变化。同时,逆变系统采用电压外环–电流内环的双闭环控制策略,能控制输出电流波形,提高系统动态响应速度,实现电流的快速检测,抑制电网电压扰动,确保逆变器输出功率因数趋于1。
文献[35] 提出一种将嵌入式重复控制器与状态反馈相结合,并加入直流电压前馈解耦和电网电压前馈补偿的方案,能消除滤波器谐振峰,抑制系统中由于直流侧脉动、电网扰动及开关管死区效应等注入的低次谐波干扰,实现系统无静差跟踪和快速响应。文献[28] 和文献[4] 提出了状态反馈极点配置与重复控制相结合的复合控制策略。通过极点配置,使逆变器阻尼增大,从而得到满意的动态性能;通过重复控制器,改善系统的稳定性,减小了非线性负载等因素造成的谐波失真,提高并网输出电流的波形质量。
文献[36] 针对逆变器谐波总畸变率(THD)过大等问题,创新地结合无差拍控制和重复控制的优点,提出了改进的复合控制策略,该系统THD小于1%,具有很强的带不平衡负载能力。文献[31] 针对负载扰动所导致的系统波形跟踪不良的问题,将无差拍控制和重复控制相结合,无差拍控制用来提高系统的动态性能,重复控制用来改善系统的稳态特性。
模糊控制较早应用在波形控制方面,有学者将模糊控制和无差拍控制结合使用,由模糊控制补偿无差拍控制在非线性负载时的误差,降低非线性负载时的波形失真;文献[24] 将模糊控制和PI控制结合,大大降低了输出波形的畸变。
5. 复合控制策略的比较
文献[31] 对逆变系统波形控制策略进行了综合比较与分析,在额定阻性负载下,无差拍控制、PID控制、模糊PID控制、重复控制和复合控制这些控制策略均能使逆变系统输出较为理想的波形,复合控制不具有很明显的优势;但在非线性负载(如整流性负载)下,复合控制系统的输出波形明显优于采用单一空着策略系统的输出波形。文献[28] 和文献[4] 对状态反馈极点配置与重复控制、PI控制与重复控制的复合控制策略进行了对比分析。
6. 结论
PWM并网逆变器的每种复合控制策略由多种(2种或2种以上)单一控制策略相互取长补短、相互配合构成。单一控制策略在电能质量控制、系统稳定性、系统响应速度、系统的鲁棒性等方面存在的问题,复合控制器从不同角度解决了上述问题,提高了并网逆变器的性价比,改善了微网并网系统的电能质量。本文对在不同电气环境下,并网逆变器控制策略的选用提供了参考。集成当前各种逆变控制技术的复合式控制技术,是未来智能电网中微网并网逆变技术研究的发展方向。