1. 引言
给水系统是浮动核电站二回路系统重要组成部分,其安全可靠的供水直接关系到平台可靠持续运行,同时也关系到反应堆的安全性。在给水系统设计时,需要对导致给水流量减少或增加的某些瞬态工况进行分析,一是确保给水系统的配置容量满足瞬态要求,不会导致蒸汽发生器水位低低或高高。二是将给水系统瞬态计算结果作为核岛瞬态安全分析的输入 [1] ,确保核岛系统的设计使堆芯不会发生DNB (偏离泡核沸腾) [2] 。
Flowmaster软件能对流体系统的流量、压力和温度分布进行精确计算并能对稳态、瞬态进行模拟 [3] [4] 。在大亚湾及岭澳核电站工程中,法国ALSTOM公司以及国内电站设计人员利用此软件对核电站常规岛进行瞬态计算 [5] [6] ,为常规岛系统优化设计提供了指导。基于上述工程应用的成功经验,采用Flowmaster软件对浮动核电站给水系统进行瞬态分析。
2. 浮动核电站给水系统及控制方式
2.1. 系统描述
给水系统配置有一台除氧器、一台高压给水加热器、两台蒸汽发生器、四台电动给水泵以及两台主给水调节阀等。给水泵的容量为33.3% * 4 (三用一备),采用变频调节。给水量通过调节给水泵的转速和给水阀的开度来控制。
给水系统流程:凝给水从除氧器中进行除氧后经过给水泵、高压给水加热器后分成两路,分别通过一台给水调节阀进入蒸汽发生器。
2.2. 控制方式
参照现有电厂运行控制方式 [7] ,拟采取的控制方式为:通过三个PID控制器来实现给水系统全程控制。高负荷时采用给水流量、蒸汽流量以及蒸汽发生器水位的三冲量调节PI1。当负荷达到一定值时,主给水调节阀达到额定流量开度,此时采用PI2直接调节给水泵的转速控制给水量。低负荷时,负荷变化小,假水位现象不严重,采用水位信号的PI3单冲量控制。在研究100%负荷给水泵切换工况时,由于给水调节阀处于可调的最大开度位置,故采用PI2直接调节给水泵转速控制给水量。
3. 系统建模
3.1. 稳态模型
依据给水系统的流程,利用Flowmaster软件建立从除氧器出口到蒸汽发生器出口的给水系统稳态模型,如图1所示。对于不同瞬态工况,在此稳态模型的基础上进行修正。
3.2. 瞬态模型
依据核电站设计经验,主给水系统瞬态分析一般包括8种工况 [8] ,其中属于给水系统自身故障的且导致蒸汽发生器上水量(水位)有较大变化的工况有:给水泵跳闸备用泵可用;给水泵跳闸备用泵不可用;零负荷时给水调节阀故障全开;满负荷时给水调节阀故障全开;主给水管道断裂事故。前两种工况主要是确保给水泵切换瞬态下,反应堆不发生跳停。后三种工况主要是为了获取“极限给水流量”,作为核岛瞬态安全分析的保守输入。其中主给水管道断裂事故一般是指双端断裂事故,此时蒸汽发生器无主给水注入,直到蒸汽发生器低低水位,反应堆停堆 [9] 。对核岛进行主给水管道断裂事故瞬态分析时,这段时间的蒸汽发生器的水量可按蒸汽发生器的储水量计算,因此将对上述前四种给水系统故障瞬态进行分析。图中纵坐标轴数值均为归一化值,即实际压力(P)、流量(G)、水量(Q)、水位(L)、转速(n)与额定工况下对应值(用带下角标0的字符表示)的比。
模拟工况1:机组在100%负荷运行时,其中一台给水泵突然跳闸,备用泵连锁启动。当t = 10 s时,一台泵跳闸,泵的跳闸转速曲线如图2所示。延迟6 s后,备用泵启动,备用泵的启动转速曲线如图2所示。延迟2 s正常运行泵开始加速,在如图1所示的稳态模型基础上加装PID控制器来控制正常泵的转速,
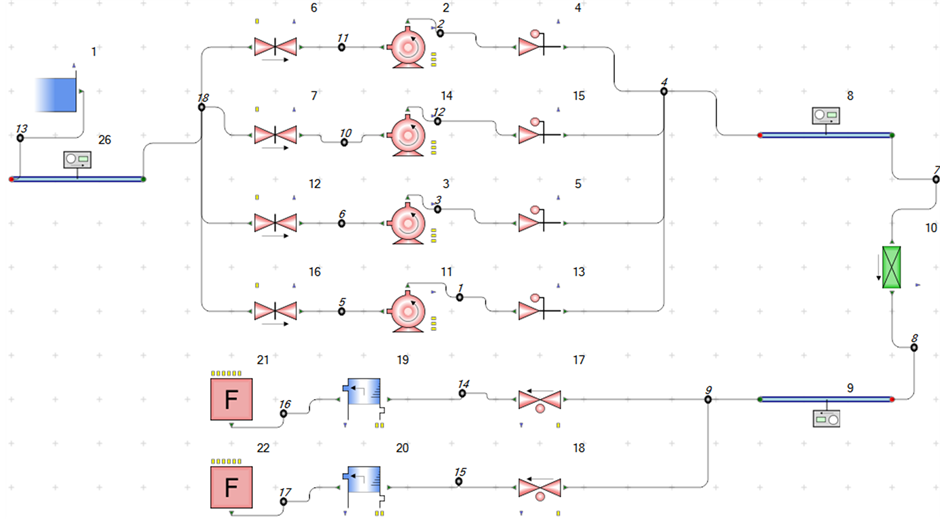
Figure 1. Model: The floating nuclear power plant main water feeding system
图1. 浮动核电站主给水系统模型图
采用PI2控制器,输入信号是蒸汽发生器水位,用信号发生器获取蒸汽发生器水位信号,输出是给水泵的转速。
模拟工况2:机组在100%负荷运行时,其中一台给水泵突然跳闸,备用泵连锁启动失败。当t = 10 s时,一台泵跳闸,泵的转速曲线如图2中的跳闸曲线所示。延迟6 s,汽轮机开始甩负荷,假设甩负荷速率是100%/min,最终降至70%负荷。延迟2 s,正常运行泵开始加速。在稳态模型的基础上加装信号控制器,模拟蒸汽发生器的介质参数。不同时刻的蒸汽发生器的压力、出口流量分别按照该时刻对应负荷下的蒸汽发生器静态特性曲线上所对应的压力、蒸汽流量来选取,如图3、图4所示。给水泵的转速采用PID控制器控制,采用PI2控制器,输入信号是蒸汽发生器水位,输出是给水泵的转速。
模拟工况3:蒸汽发生器带零负荷工况,给水调节阀以及所有给水旁路阀均处于关闭状态。在t = 0 s时,主给水调节阀故障全开,给水泵在额定转速运行。在稳态模型基础上,用信号控制器模拟蒸汽发生
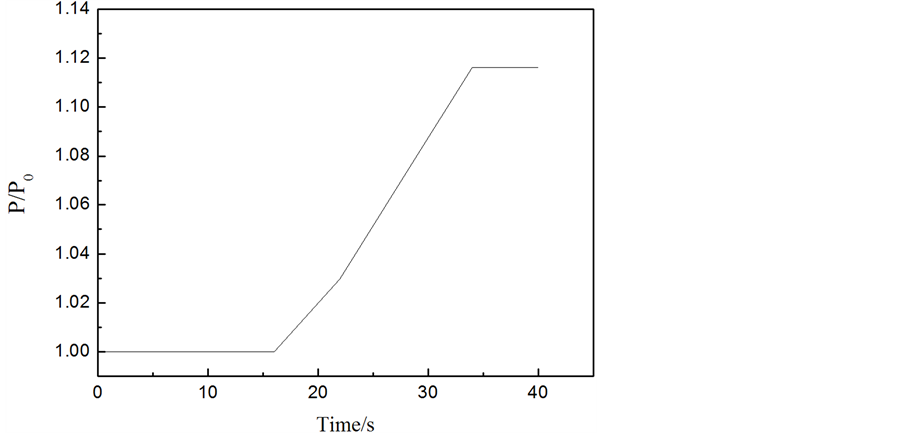
Figure 3. Curve: Steam generator pressure versus time
图3. 蒸汽发生器压力变化曲线
器的压力,假设蒸汽发生器的泄压速率为0.10 MPa/s。
模拟工况4:蒸汽发生器带满负荷工况,三台给水泵在额定转速运行,两台主给水调节阀处于60%开度。在t = 0 s时,一台主给水调节阀故障全开。假设蒸汽发生器的泄压速率为0.01 MPa/s。
4. 瞬态结果分析
工况1结果分析:一台主给水泵跳闸后,如图5所示给水量瞬间减少,蒸汽发生器水位逐渐降低。在水位差信号作用下正常运行泵延迟2 s后开始加速,正常运行泵的转速如图6所示,在跳泵后6 s内达到最高转速。由于备用泵的启动以及正常运行给水泵的加速,给水量逐渐增加,直到约160 s时蒸汽发生器水位恢复额定水位,所有泵转速均恢复到额定转速,给水量恢复到要求上水量。同时,从图5可以看出,给水系统很快重回稳定工况,在此过程中最大的失水量约为0.05 m3,满足失水量 < 0.340 m3要求。
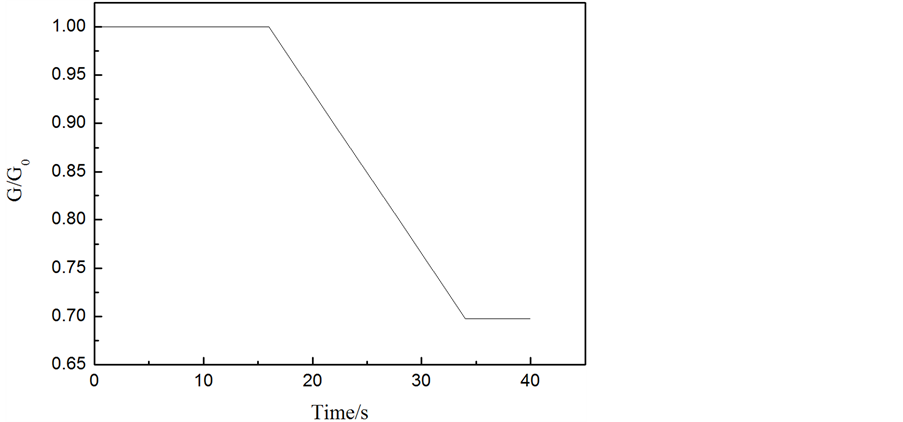
Figure 4. Curve: Steam flow at the steam generator outlet versus time
图4. 蒸汽发生器出口蒸汽流量变化曲线
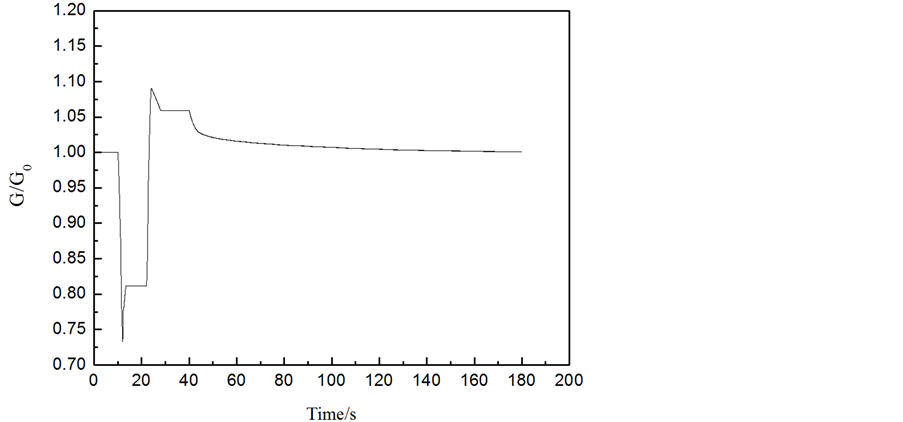
Figure 5. Curve: Steam generator water supply versus time
图5. 蒸汽发生器的上水量变化曲线
工况2结果分析:如图7所示,一台给水泵在10 s时跳闸,给水流量大幅降低(如图8),导致蒸汽发生器的上水量低于蒸汽发生器的出口蒸汽量,使得蒸汽发生器内的水量逐渐减低。但随着负荷降低,蒸汽发生器出口蒸汽量也在逐渐减少(如图5),约30 s后,蒸汽发生器的上水量高于出口蒸汽量,故蒸汽发生器水位逐渐恢复到初始水量。在蒸汽发生器的水量逐渐恢复到初始水量过程中,给水泵转速在PID控制器的作用下逐渐达到稳定转速。如图9所示,在约30 s时,蒸发器的水量损失达到最大约0.06 m3,满足失水量 < 0.34 m3要求。
工况3结果分析:蒸汽发生器水位达到高高限值1.07 (L/L0),反应堆立即跳停,主给水隔离阀关闭。由图10可知,在t = 5.7 s时,水位达到高高限值,此时最大的给水流量为额定流量的1.06%。因此,在此瞬态下,考虑一定裕量,核岛安全分析时可输入信号:给水量从0%阶跃增加到110%额定流量。
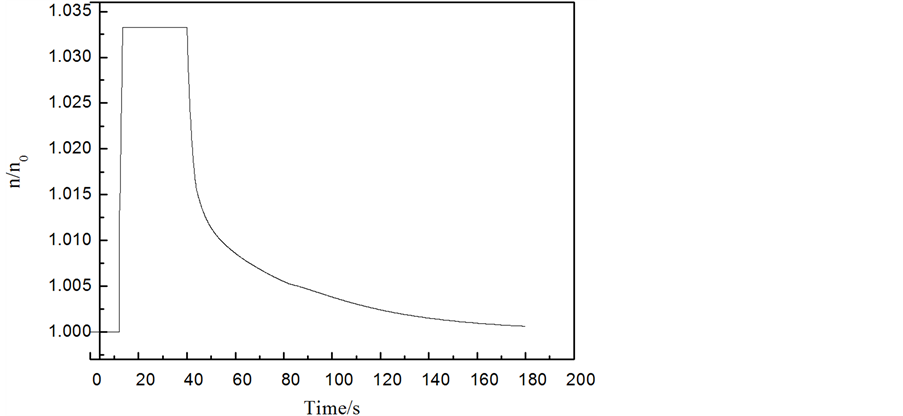
Figure 6. Curve: Normal running pump speed versus time
图6. 正常运行泵的转速变化曲线
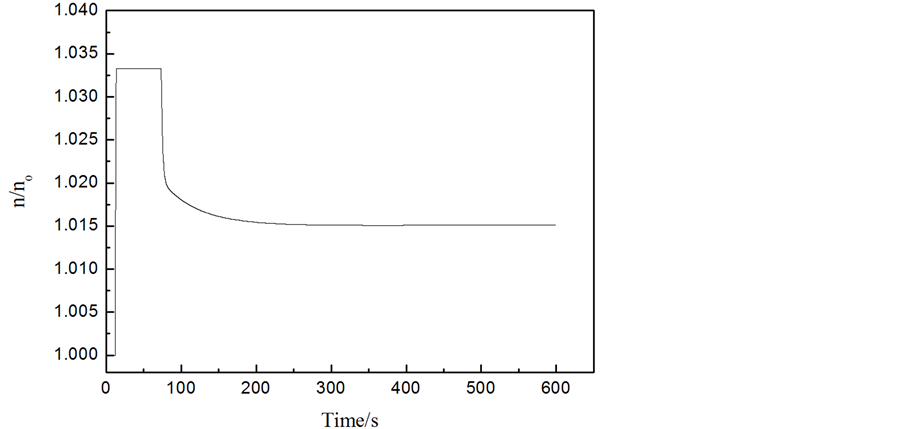
Figure 7. Curve: Normal running pump speed versus time
图7. 正常运行泵的转速变化曲线
工况4结果分析:蒸汽发生器水位达到高高限值1.07 (L/L0),反应堆立即跳停,主给水隔离阀关闭。由图11可知,在t = 18.86 s时,水位达到高高限值,此时最大的给水流量为额定流量的115%。由图11可以看出在满负荷时调节阀故障全开达到“跳堆”信号时间较长,给水量在1~1.15之间。将最大给水流量作为核岛安全分析输入时已经取了较大的裕量,因此,此瞬态下,核岛安全分析时可输入信号:给水流量阶跃增加到115%额定流量。
5. 结论
通过Flowmaster对给水系统的四种典型故障瞬态进行了分析,可以得出以下结论:
1) 给水泵跳闸后,备用泵正常启动或不能启动,失水量都远小于最大允许失水量0.34 m3,可以反映
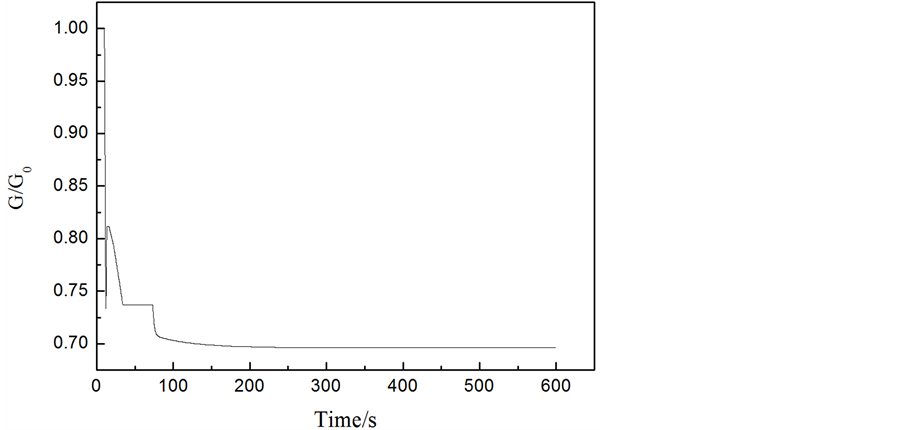
Figure 8. Curve: Steam generator water supply versus time
图8. 蒸汽发生器上水量变化曲线
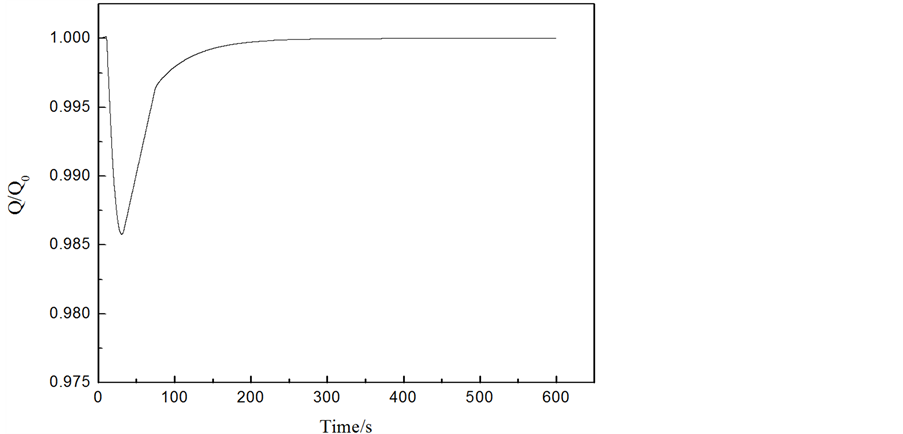
Figure 9. Curve: Steam generator water volume versus time
图9. 蒸汽发生器的水量变化曲线
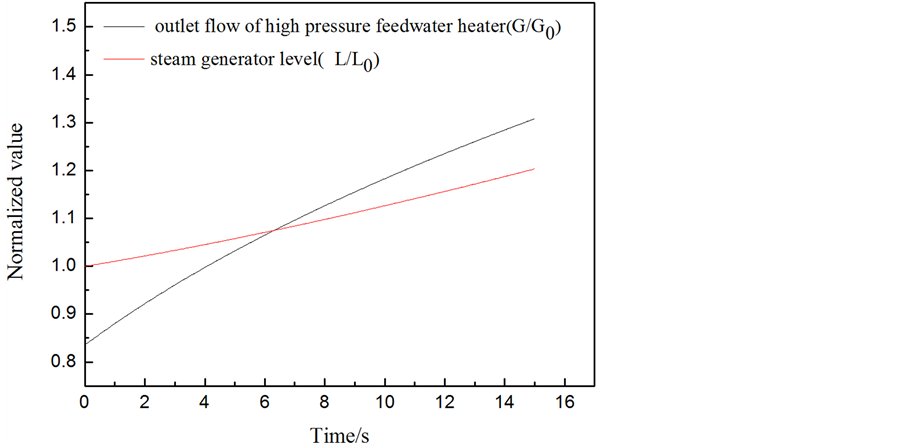
Figure 10. Curve: The simulation result of condition of main feed-regulating valve fully open under no load
图10. 零负荷时给水调节阀故障工况全开模拟结果
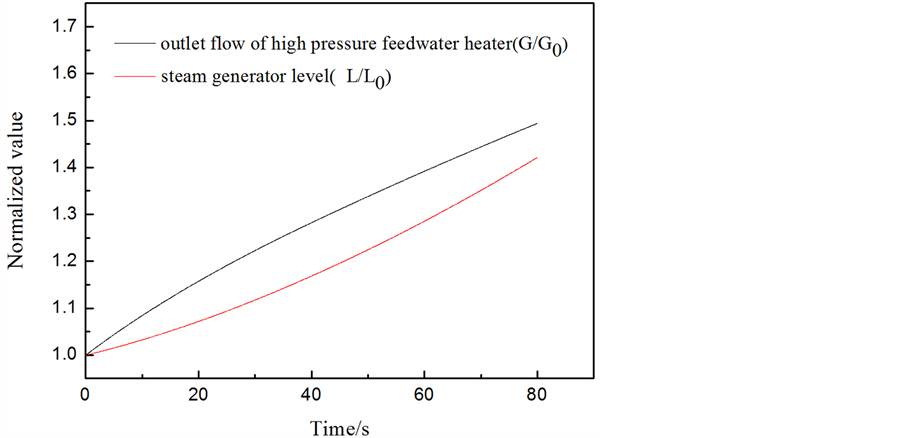
Figure 11. Curve: The simulation result of condition of main feed-regulating valve fully open under full load
图11. 满负荷时给水调节阀故障全开工况模拟结果
出目前给水系统给水泵的配置数量和容量满足系统设计要求;
2) 蒸汽发生器带零负荷工况时,一台主给水调节阀故障全开瞬态工况,核岛安全分析输入信号可设置为:给水流量从0%阶跃增加到110%额定流量。可用于核岛设计的输入,保证此瞬态下堆芯不会发生DNB;
3) 蒸汽发生器带满负荷工况时,一台主给水调节阀故障全开瞬态工况,核岛安全分析输入信号可设置为:给水流量阶跃增加到115%额定流量。可用于核岛设计的输入,保证此瞬态下堆芯不会发生DNB。
基金项目
国家科技支撑计划项目(2012BAA14B00)。