1. 引言
石上柏(Selaginella doederleininii)是蕨类卷柏科卷柏属(Selaginella doederleinii Hieron.)植物深绿卷柏的全草,为我省使用悠久的苗药之一。本药材甘、涩,性温平,主治咽喉肿痛,目赤肿痛,肺热咳嗽,湿热黄疸,风湿痹痛 [1] [2]。石上柏又称“深绿卷柏”、“地侧柏”、“梭罗草”、“龙鳞草”、“大叶菜”,其生长环境较阴湿,多生长于林下、沟边的阴石上,在南方地区分布较多,如贵州、四川、云南、福建等地 [3]。据大量学者报道,石上柏具有抗肿瘤、抗炎、抗氧化等药理作用 [4]。因此,明确其化学本质以及药理作用对充分利用石上柏具有重要意义。本文主要对石上柏的化学成分、药理作用进行整理、分析。
2. 石上柏的化学成分
石上柏含有多种生物活性成分,主要包括双黄酮类、生物碱、木脂素、有机酸等化合物 [5]。
2.1. 黄酮类
双黄酮类化合物广泛存在于卷柏属植物中,是石上柏的主要活性成分 [6],具有抗心肌缺血,抗肿瘤、抗氧化等作用 [7] [8]。双黄酮是黄酮类化合物的二聚体,由黄酮单体通过化学键(C-C-C/C-O-C)连接而成 [4]。目前已在石上柏中分离出的黄酮类化合物已达40余种(化学成分名称见表1、结构式见图1~41),主要由穗花杉双黄酮、罗波斯塔黄酮-2'',3''-二氢-3',3'''-联芹菜素、3',3'''-双柚皮素等组成,比例分别为10.38%、3.75%、4.44%、5.35% [9]。Liu [10] [11] 等最近从石上柏中分离得到黄酮类化合物,其中有三个双黄酮(1-3)为首次分离得到,通过对人癌细胞系(A549,MCF-7和SMMC-7721)和非致瘤细胞评估其细胞毒性,得到化合物1和3的细胞毒性微弱,化合物2表现出强力的细胞毒性,IC50值分别为7.86 µM、6.35 µM和10.18 µM。

Table 1. Name and structure of Selagintriflavonoids
表1. 石上柏双黄酮的名称与结构

Figure 1. Structural formula of Amentoflavone
图1. Amentoflavone结构式
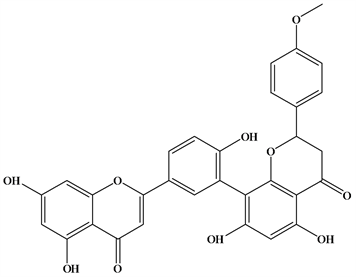
Figure 2. Structural formula of Podocarpusflavone
图2. Podocarpusflavone结构式
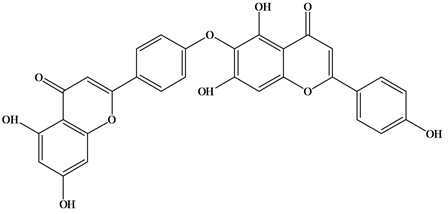
Figure 3. Structural formula of Hinokiflavone
图3. Hinokiflavone结构式
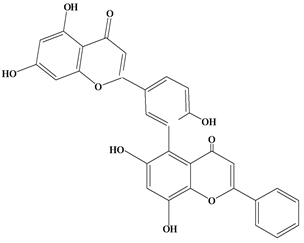
Figure 4. Structural formula of Apigenin-(3′,8″)-chysin
图4. Apigenin-(3′,8″)-chysin结构式
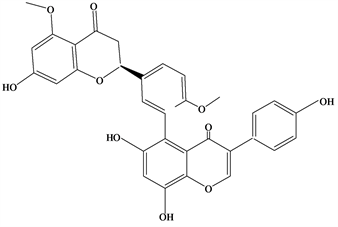
Figure 5. Structural formula of (2S)-2,3-Dihydroametoflavone 5,4′-dimethyl ether
图5. (2S)-2,3-Dihydroametoflavone 5,4′-dimethyl ether结构式
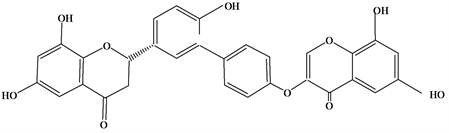
Figure 6. Structural formula of (2S)-5′′,7′′-Dihydroxy-2′′-phenoxychomonyl-(4′′′,3′)-naringenin
图6. (2S)-5′′,7′′-Dihydroxy-2′′-phenoxychomonyl-(4′′′,3′)-naringenin结构式

Figure 7. Structural formula of Heveaflavone
图7. Heveaflavone结构式
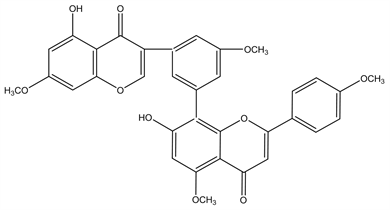
Figure 8. Structural formula of 7,4′,7′′,4′′′-tetra-O-methylamentoflavone
图8. 7,4′,7′′,4′′′-tetra-O-methylamentoflavone结构式
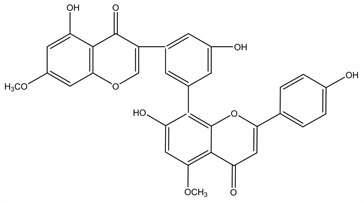
Figure 9. Structural formula of 7,7′′-di-O-methylamentoflavone
图9. 7,7′′-di-O-methylamentoflavone结构式

Figure 10. Structural formula of Robustaflavone-4′′-O-methyl ether
图10. Robustaflavone-4′′-O-methyl ether结构式
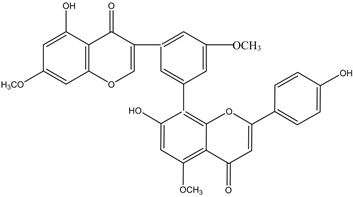
Figure 11. Structural formula of 2,2′,3′′,3′-Tetrahydrorobustaflavone
图11. 2,2′,3′′,3′-Tetrahydrorobustaflavone结构式
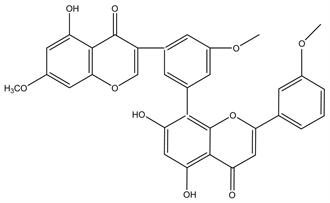
Figure 13. Structural formula of Isoginkgetin
图13. Isoginkgetin结构式

Figure 15. Structural formula of Podocarpusflavone A
图15. Podocarpusflavone A结构式

Figure 16. Structural formula of Putraflavone
图16. Putraflavone结构式
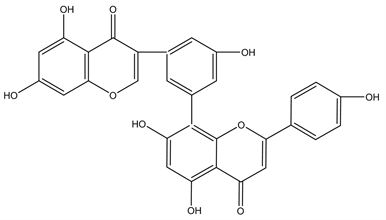
Figure 17. Structural formula of Robustaflavone
图17. Robustaflavone结构式

Figure 18. Structural formula of Robustaflavone-7,4′,7″-trimethyl ether
图18. Robustaflavone-7,4′,7″-trimethyl ether结构式
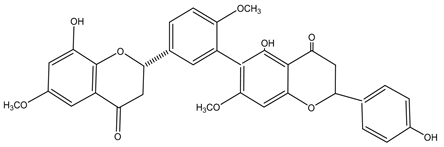
Figure 19. Structural formula of 2,2″,3,3″-tetrahydrorobustaflavone-7,4′,7″-trimethylether
图19. 2,2″,3,3″-tetrahydrorobustaflavone-7,4′,7″-trimethylether结构式

Figure 20. Structural formula of 7″-methylrobustaflavone
图20. 7″-methylrobustaflavone结构式
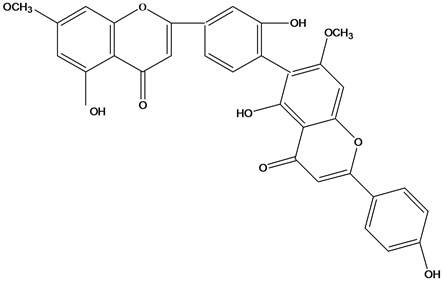
Figure 21. Structural formula of 7,7″-di-O-methylrobustaflavone
图21. 7,7″-di-O-methylrobustaflavone结构式

Figure 22. Structural formula of 7″,4″'-di-O-methylrobustaflavone
图22. 7″,4″'-di-O-methylrobustaflavone结构式
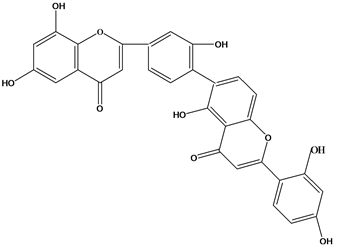
Figure 23. Structural formula of 2′′,3′′-dihydro-3′,3′′′-biapigenin
图23. 2′′,3′′-dihydro-3′,3′′′-biapigenin结构式
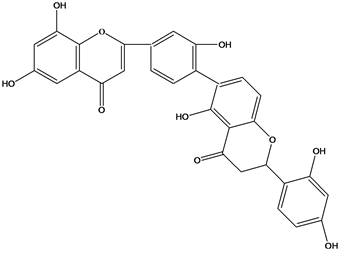
Figure 24. Structural formula of 3′,3′′′-binaringenin
图24. 3′,3′′′-binaringenin结构式

Figure 26. Structural formula of Isopimpinellin
图26. Isopimpinellin结构式
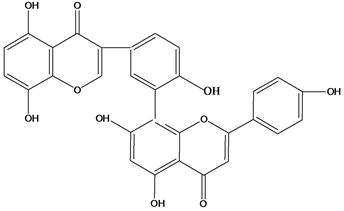
Figure 27. Structural formula of 4′,4′′′,5,5′′,7,7′′-hexahydroxy-2′,8′′-biflavon
图27. 4′,4′′′,5,5′′,7,7′′-hexahydroxy-2′,8′′-biflavon结构式

Figure 28. Structural formula of 4′,4′′′,5,5′′,7,7′′-hexahydroxy-2′,6′′-biflavone
图28. 4′,4′′′,5,5′′,7,7′′-hexahydroxy-2′,6′′-biflavone结构式
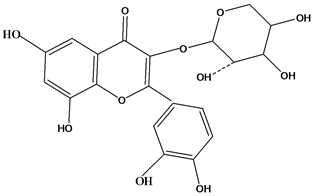
Figure 29. Structural formula of Quercetin-3-O-α-D-arabinopyranoside
图29. Quercetin-3-O-α-D-arabinopyranoside结构式

Figure 31. Structural formula of Chysocauloflavone I
图31. Chysocauloflavone I结构式

Figure 32. Structural formula of Delicaflavone
图32. Delicaflavone结构式
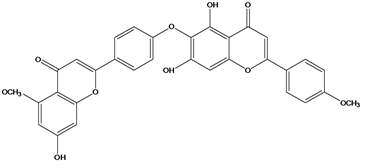
Figure 33. Structural formula of 7,4′′′-di-O-methylhinokiflavone
图33. 7,4′′′-di-O-methylhinokiflavone结构式
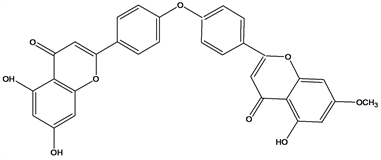
Figure 34. Structural formula of Loniflavone
图34. Loniflavone结构式
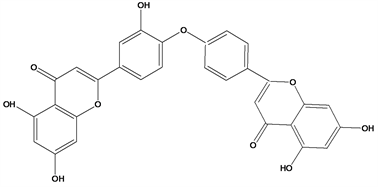
Figure 35. Structural formula of 7′′-methylloniflavone
图35. 7′′-methylloniflavone结构式

Figure 36. Structural formula of 3′-methylloniflavone
图36. 3′-methylloniflavone结构式结构式

Figure 37. Structural formula of 7,7′′-di-O-methylloniflavone
图37. 7,7′′-di-O-methylloniflavone结构式
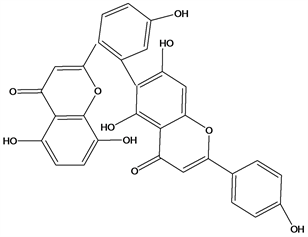
Figure 38. Structural formula of 7-methyoxylamentoflavone
图38. 7-methyoxylamentoflavone结构式

Figure 39. Structural formula of 4′,7′′-di-O-methylamentoflavone
图39. 4′,7′′-di-O-methylamentoflavone结构式
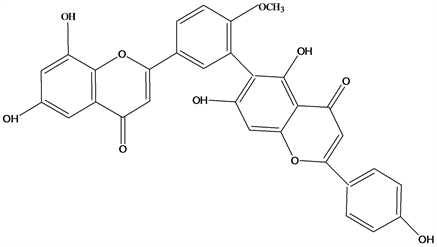
Figure 40. Structural formula of 7,4′,7′′-tri-O-methylamentoflavone
图40. 7,4′,7′′-tri-O-methylamentoflavone结构式结构式

Figure 41. Structural formula of Robustaflavone 4′-methyl ether
图41. Robustaflavone 4′-methyl ether结构式
2.2. 木质素类化合物
木质素(Lignan)别名木质体,是石上柏植物中的活性物质,是存在于自然界中的一类植物雌激素,常以二聚体的形式存在 [17]。其结构是由二分子苯丙素衍生物(C6-C3)聚合而成,在植物中以小分子次生代谢产物存在,活性多样。
Le [18] 等从卷柏属植物中分离出5种木质素苷衍生物和一种新的木质素鹅掌楸碱,根据这些化合物在巨噬细胞系RAW 264.7中对脂多糖(LPS)刺激的活性中NO生成的抑制作用进行了评估,并通过实验表明木质素苷化合物对NO有抑制作用。此外,国外学者Kim等 [19] 从石上柏植物中分离得到里立脂素A等7个木脂素化合物;Wei [20] [21] 等提取分离得到一种新的木脂素Selamoellenin A,作者评估了Selamoellenin A对高葡萄糖诱导的HUVEC损伤的保护作用,结果表明Selamoellenin A在10-1,10-2,10-4和10-5 μM的浓度下显示出有效的保护作用。
2.3. 生物碱类化合物
生物碱是主要存在于植物中的一类含氮的碱性有机化合物,通常为氮原子结合在环内且具有较为复杂的环状结构。石上柏中生物碱的活性成分主要是大麦芽碱类,具有收缩血管,松弛支气管平滑肌等作用,并且具有光学活性 [22] [23] [24]。Li [25] 等学者在卷柏属植物中发现了芥子油酸、5-羟基芥子油酸、5-羟基-N 8,N 8-二甲基伪苯丙胺基、N-芥子油基-L-苯丙氨酸等八种新的吡咯烷基吲哚啉生物碱。石上柏还含有大麦芽碱等六个生物碱类化合物 [26],目前大麦芽碱类生物碱在植物中存在不多,只在少数植物如大麦、仙人掌、含羞草等中有发现 [27] [28],其药理作用还有待研究者探索。
2.4. 有机酸类化合物
有机酸类(Organic acids)是分子结构中含有羧基(-COOH)的化合物,多溶于水或乙醇呈显著的酸性,难溶于其它有机溶剂。石上柏中分离得到的有机酸类化合物分别是软脂酸、硬脂酸、莽草酸和大叶菜酸等,具有较好的药理作用,如抗氧化等。有趣的是,在结构上大叶菜酸是莽草酸聚合后的产物 [29] [30],其两者可能存在一定的转化关系,使石上柏的药理作用更全面。
2.5. 其他
通过GC-MS分析石上柏共得到71个化合物,共鉴定出64个化合物,其相对峰面积分别占总峰面积的98.19%,主要包括萜类,脂肪酸及其烃类化合物 [31]。
3. 药理性质
3.1. 抗肿瘤作用
研究发现,石上柏具有较好的抗肿瘤作用,目前研究者基于石上柏抗肿瘤这一活性作用,在抗肿瘤方面做了许多研究工作,具有较好的开发前景。石上柏在临床上用于治疗肺癌、肝癌及鼻咽癌等肿瘤疾病。Chen [9] 等将石上柏总双黄酮作用于结肠癌细胞以及大鼠的结肠癌模型中,药效学结果表明,TBESD (石上柏总双黄酮)和(石上柏总双黄酮脂质体) P-TBESD组均具有抗肿瘤作用而无全身毒性,基于肿瘤生长抑制和组织病理学检查,P-TBESD的抗肿瘤作用明显优于未处理的TBESD。此外,不同产地石上柏挥发油对A549和7721细胞株具有一定的抑制作用,其中抑制A549细胞最高的IC50为46.81 mg·L−1;抑制7721细胞最高的IC50为34.02 mg·L−1。通过OPLS和Bivariate数据分析,发现5个挥发油成分,即芳樟醇、橙花叔醇、新植二烯、亚油酸甲酯、植酮,与石上柏挥发油抑制肺癌A549细胞和肝癌7721细胞活性显著相关 [32] [33]。
Sui [34] 等研究发现,在BALB/c裸鼠的人非小细胞肺癌异种移植模型中,石上柏双黄酮可通过Akt/mTOR/p70S6K信号通路诱导人非小细胞肺癌中的自噬细胞死亡,从而发挥抗癌作用,且无不良反应。Lian [35] 等利用石上柏乙醇提取物对两种鼻咽癌细胞株CNE-1和C666-1增殖的影响进行了研究,结果表明,高浓度组的2.5 μg/mL提取物表现出与CNE-1细胞上的浓度成正比且具有抑制作用,而相对于C666-1细胞没有明显的成比例趋势。Hong [36] 等通过MTT测定法和雄性C57BL/6小鼠肺癌LLC的异种移植模型验证了石上柏总双黄酮提取物的体外和体内抗癌活性,均能增强小鼠肺癌模型的抗肿瘤免疫反应。Chen [37] 等从石上柏中提取出总双黄酮,通过改良制剂的方法提高双黄酮的生物利用度,在大鼠中进行的药代动力学研究表明,石上柏双黄酮对携带异种移植的肿瘤小鼠肿瘤大小和微血管密度显著降低,提示石上柏可能是一种有前景的癌症治疗药物。
3.2. 抗氧化
研究发现,深绿卷柏总黄酮对羟基自由基、超氧阴离子自由基、DPPH自由基的清除率随总黄酮作用浓度升高而增强,EC50 (半数清除率)分别为111.86 μg/mL、89.24 μg/mL、26.51 μg/mL [38]。银杏双黄酮是一种天然抗氧化剂,其能够维持人体内自由基平衡,提高细胞内超氧化物歧化酶的活性、减少细胞的过氧化、具有抗氧化作用。有学者 [39] 采用DPPH自由基清除法测试石上柏双黄酮混合物结晶抗氧化活性,以抗坏血酸作为阳性对照,在浓度为52.3 μg/mL时,对DPPH自由基的清除率为8.0%,抗坏血酸达到95.5%。研究发现 [36],穗花杉双黄酮对DNA、胞嘧啶、尿嘧啶、腺嘌呤、胸腺嘧啶、鸟嘌呤、鸟嘌呤的IC50值分别为31.85 ± 4.75 μM、198.75 ± 33.53 μM、147.14 ± 20.95 μM、75.15 ± 10.52 μM、93.75 ± 16.36 μM、167.69 ± 13.90 μM和137.95 ± 19.86 μM。自由基清除试验表明,穗花杉双黄酮能有效清除O2−、DPPH、ABTS+自由基,IC50值分别为8.98 ± 0.23 μM、432.25 ± 84.05 μM、7.25 ± 0.35 μM。
3.3. 抗炎
许兰 [40] 等发现石上柏不同溶剂(己烷、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇)提取物有明显的舒张血管作用,其中以乙酸乙酯提取物(100 mg/mL)舒张血管作用最强,且有NO参与。石上柏醇提物160、80、40 mg/kg均可以明显改善小鼠心肌组织的病理性损伤情况,TTC染色结果发现,不同剂量组可以显著减少小鼠心肌缺血区的面积;与模型组相比,血清中LDH和CK-MB水平显著降低(p < 0.05、0.01),对小鼠急性心肌缺血有一定的保护作用。从1971年起 [41],广州市第一人民医院对石上柏提取物进行临床作用研究发现:石上柏提取物对急性扁桃腺炎、上呼吸道炎、症肺炎等炎症具有较好的治疗效果,具有明显的抗炎作用,对各种炎症治疗达300多例,其中有效率94.2%,治愈率54%,且暂时没有发现不良反应。
石上柏抗炎作用成分中,报道最多的是双黄酮成分,Zou等 [15] 在检测黄酮抗炎作用的研究中以NF-κB的活性作为考察指标,结果发现异银杏黄素和银杏黄素在20 μM的初始筛选中表现出抑制作用,而银杏黄素的抑制作用远大于异银杏黄素。在剂量反应实验中,银杏黄素的IC50值为7.5 μM,表明双黄酮可能是一种强的NF-κB抑制剂。研究发现,银杏双黄酮对COX-2/5-LOX具有双重抑制特性,可增强抗炎效果,并且能减轻与非甾体抗炎药物的类似不良反应,增强疗效。穗花杉双黄酮可通过下调COX-2的表达,抑制PGE2的生成 [42]。Sakthivel等 [43] 从日本金银花中分离得到的银杏木双黄酮,研究发现其能下调IκB激酶-α (IKK-α)活性,对内毒素(LPS)诱导的磷酸化有抑制作用,并且对IKK-α有降解作用,从而抑制NF-κB活化作用,达到抗炎的效果。
Woo [44] 等研究发现穗花杉双黄酮对超氧阴离子和总活性氧(ROS)的Inphorbol 12-肉豆蔻酸13-乙酸盐刺激的人中性粒细胞产生抑制作用。在2,2'-偶氮双(2-ami基丙烷)盐酸盐诱导的人红细胞中,穗花杉双黄酮还能抑制氧化剂的溶血和脂质过氧化作用。在大鼠星形细胞瘤细胞系中,脂多糖(LPS)可以增加NO、ROS、丙二醛(MDA)的水平,并降低还原型谷胱甘肽(GSH)的含量,而人单核细胞白血病细胞系中LPS增加了肿瘤坏死因子-α (TNF-α)的产生,上述所有变化均被双黄酮显著减弱,对细胞没有明显的影响 [45]。在用LPS刺激的RAW 264.7细胞中,观察到黄酮能抑制NO水平、前列腺素E-2 (PGE-2)的产生以及c-Fos (活化蛋白(AP)-1的亚基)的核易位,c-Fos易位的细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)被活性双黄酮抑制。在人外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)的上清液中,黄酮可以抑制植物血凝素(PHA)诱导的白介素-1β (IL-1β)、IL-6、TNF-α和PGE2的升高 [18]。
3.4. 其他
Pan [46] 等在穗花杉双黄酮通过抑制骨肉瘤U2OS细胞中ERK/NF-κB的活化抑制其转移潜力的研究中发现,抑制细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)的激活是抑制NF-κB调节转移机制的关键。结果表明穗花杉双黄酮可显著抑制ERK磷酸化从而抑制NF-κB活化,并抑制相关蛋白的表达以及细胞迁移和侵袭。研究发现 [5],石上柏可产生各种具有不同生物活性的次级代谢产物,这些潜在代谢产物可能用于治疗多种疾病,已经在几种糖尿病小鼠模型中研究了抗糖尿病活性,在该模型中,它可以有效缓解高血糖症、葡萄糖耐受不良反应、胰岛素抵抗、血脂异常和胰岛肥大。蝶呤A可以抑制糖尿病小鼠体重的减少以及饲喂小鼠和糖尿病小鼠的体重的增加。此外,它逆转了糖尿病相关的糖尿病小鼠骨骼肌中GLUT-4从细胞质到膜的转运减少以及肝脏中PEPCK表达的增加。GLUT-4并由翼蛋白A抑制肝PEPCK表达,翼蛋白A也增加GSK3磷酸化,进一步增强肝细胞内细胞内糖原合成。
4. 结语
综上所述,石上柏的生物价值等各方面的研究有很大的发展空间,且在国内是个新热点。大量研究表明,石上柏具有活血通经、化瘀止血等功效,效果显著,且对其不良反应鲜有文献报道。石上柏主要发挥作用的化学成分为双黄酮,结合大量资料对石上柏中双黄酮成分的药理作用研究显示,该化合物可以通过多种途径发挥抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤等作用。对上述化学成分的药理作用和性质加以研究整合,于科研工作者来说,继续对其化学本质的深入研究,进而发现前人未发现的理化作用是有可能的。希望该文的整理与分析为石上柏植物的研究提供参考,并且对以双黄酮类化合物为基础的新药研发具有一定的指导意义。
致谢
首先我要诚挚地感谢我的导师王刚教授,导师渊博的知识、深厚的学术造诣、扎实的理论功底一直深深影响着我,他严谨的治学态度和高尚的道德情操将是我终生学习的榜样。同时,王刚老师在生活、工作、学习中的热情关怀和悉心指导使我温暖备至。此外,我也要诚挚地感谢国家自然科学基金项目的支持。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金(81860697)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。