1. 引言
肺癌是全球癌症死亡的主要原因之一,约占癌症总死亡人数的18% [1]。根据组织病理类型的不同,肺癌主要分为非小细胞肺癌(Non-small cell lung carcinoma, NSCLC)和小细胞肺癌(Small cell lung carcinoma, SCLC),而NSCLC是肺癌主要的病理类型 [2]。目前肺癌的治疗方法有手术、化疗、靶向治疗、免疫疗法等,虽已显著提高了患者的生存率,但大多数确诊的晚期肺癌患者的总生存率不足20% [3]。因此,迫切需要进一步探索肺癌的发生发展机制,寻找新的治疗靶点,研发更有效的治疗药物。
可溶性N-乙基马来酰亚胺敏感性因子附着蛋白受体(Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor, SNARE)是位于细胞器和细胞膜上的一类跨膜蛋白,它可精确地调节外泌体的产生和释放。YKT6是一种从酵母到人类高度保守的SNARE蛋白质,与膜融合和囊泡运输有关,并参与外泌体的形成和释放 [4]。然而,目前关于YKT6在NSCLC中的作用的研究较少。本文利用公共数据库对YKT6在NSCLC中的表达及预后进行分析,为寻找NSCLC分子标志物及治疗靶点提供依据。
2. 材料与方法
2.1. YKT6在泛癌中的表达
下载TCGA (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov)数据库 [5] 中泛癌项目中的RNA seq数据,进行log2转化,并使用R语言中的ggplot2包对YKT6在癌症中的表达进行统计分析及可视化,分析YKT6在肿瘤组织与癌旁组织中的表达情况。
2.2. YKT6在肺癌中的表达水平
Ualcan (http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/index.html)数据库是一个全面的、用户友好的交互式网络资源,用于分析癌症OMICS数据 [6]。我们使用Ualcan数据库分析YKT6在LUAD及LUSC中的表达水平。HPA (https://www.proteinatlas.org)数据库是利用转录组学和蛋白质组学技术,从RNA和蛋白水平研究人类不同组织和器官中的蛋白表达情况的开放性数据库 [7]。我们使用HPA数据库分析并比较NSCLC组织和正常组织中YKT6蛋白的表达水平。
2.3. YKT6表达水平和临床病理特征的关系
为了进一步探索YKT6的表达水平与临床病理特征的关系,我们使用Ualcan网站进行分析。首先打开网址,选择TCGA,基因输入YKT6,癌症设为Lung adenocarcinoma、Lung squamous cell carcinoma,探究YKT6表达水平与临床分期的关系。
2.4. YKT6对肺癌患者诊断和预后价值
Kaplan-Meier plotter (http://www.kmplot.com)整合了GEO、TCGA等数据库的芯片数据,提供包括肺癌在内的多种癌症的预后信息。我们使用该数据库对YKT6的表达与肺癌患者预后的相关性进行分析;随后我们下载TCGA数据库中 LUAD、LUSC项目HTSeq-FPKM格式的RNAseq数据,转换成TPM格式并进行log2转化,并使用R语言pROC包分析相关资料并使用ggplot2包对结果进行分析和可视化,绘制ROC曲线。
3. 结果
3.1. YKT6在泛癌中的表达情况
为了探究YKT6与癌症之间的关系,我们分析了TCGA数据库中包含未配对肿瘤和非肿瘤组织的表达,使用R语言分析YKT6在不同癌组织中的表达情况。结果显示,与正常组织相比,YKT6在膀胱尿路上皮癌(Bladder urothelial carcinoma, BLCA)、浸润性乳腺癌(Breast invasive carcinoma, BRCA)、宫颈鳞癌和腺癌(Cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma, CESC)、胆管癌(Cholangiocarcinoma, CHOL)、结肠癌(Colon adenocarcinoma, COAD)、食管癌(Esophageal carcinoma, ESCA)、多形成性胶质细胞瘤(Glioblastoma multiforme, GBM)、头颈鳞状细胞癌(Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, HNSC)、肾嫌色细胞癌(Kidney chromophobe renal cell carcinoma, KICH)、肾透明细胞癌(Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, KIRC)、肾乳头状细胞癌(Kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma, KIRP)、肝细胞肝癌(Liver hepatocellular carcinoma, LIHC)、LUAD、LUSC、前列腺癌(Prostate adenocarcinoma, PRAD)、直肠腺癌(Rectum adenocarcinoma, READ)、胃癌(Stomach adenocarcinoma, STAD)以及子宫内膜癌(Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma, UCEC)中均呈现较高的表达水平(见图1)。
3.2. YKT6 mRNA在NSCLC组织与正常组织中的表达情况
通过搜索Ualcan数据库,YKT6在LUAD和LUSC中的表达水平均高于正常组织(图2(a)和图2(b)),且具有显著性差异(P < 0.001)。
3.3. YKT6蛋白在NSCLC组织与正常组织的表达情况
检索HPA数据库的结果表明,在4例肺癌组织中,YKT6均呈中–高水平的表达,其中1例LUAD强染色(图3(b)),1例LUAD中等程度染色(图3(e)),2例肺鳞癌中等程度染色(图3(c)和图3(f)),而2例正常组织无明显染色(图3(a)和图3(d))。
3.4. YKT6表达与肺癌临床分期的相关性
通过Ualcan数据库分析YKT6的表达水平与临床分期的相关性。结果表明YKT6表达水平与LUAD和LUSC的临床分期均显著相关(图4(a)和图4(b))。
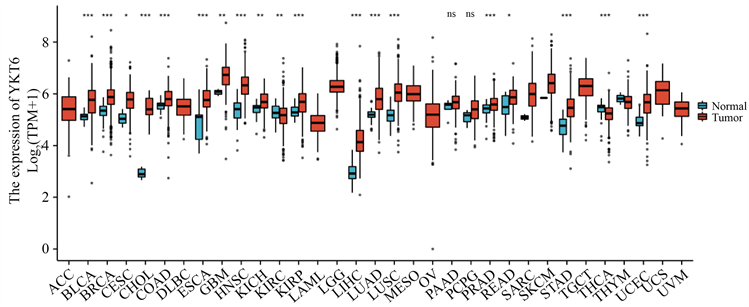
Figure 1. Expression of YKT6 in pan carcinoma
图1. YKT6在泛癌中的表达
 (a) YKT6在肺腺癌中高表达;(b) YKT6在肺鳞癌中高表达
(a) YKT6在肺腺癌中高表达;(b) YKT6在肺鳞癌中高表达
Figure 2. High expression of YKT6 mRNA in lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
图2. YKT6 mRNA在肺腺癌和肺鳞癌中高表达
3.5. YKT6表达水平与肺癌预后的相关性
我们探究了YKT6表达与肺癌患者预后之间的关系。结果表明,YKT6表达与肺癌患者总生存(Overall survival, OS) (P = 3.1 × 10−5)、首次进展生存期(First progression, FP) (P = 1.6 × 10−7)显著相关,与进展后生存期(Post progression survival, PPS)无显著相关性(P = 0.059) (图5(a)~(c));随后我们探究了YKT6表达与LUAD和LUSC患者OS、无复发生存期(Recurrence free survival, RFS)的相关性。结果表明,YKT6表达与LUAD患者OS (P = 0.00096)显著相关,与患者RFS (P = 0.072)无明显相关性(图5(c)和图5(d));而YKT6表达与LUSC患者的OS (P = 0.086)、RFS (P = 0.3)均无明显相关性(图5(e)和图5(f))。
3.6. ROC曲线
为了评估YKT6对NSCLC的诊断价值,我们绘制了接收者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve, ROC)曲线,并计算曲线下面积(Area under curve, AUC);结果显示LUAD和LUSC的AUC分别为0.864、0.842 (图6(a)和图6(b)),表明YKT6的表达对LUAD和LUSC有很好的诊断价值。
 (a) 49岁女性正常组织,低染色;(b) 51岁女性肺腺癌,强染色;(c) 66岁男性肺鳞癌,中染色;(d) 49岁女性正常组织,未检测到;(e) 49岁男性肺腺癌,中染色;(f) 65岁男性肺鳞癌,中染色。
(a) 49岁女性正常组织,低染色;(b) 51岁女性肺腺癌,强染色;(c) 66岁男性肺鳞癌,中染色;(d) 49岁女性正常组织,未检测到;(e) 49岁男性肺腺癌,中染色;(f) 65岁男性肺鳞癌,中染色。
Figure 3. High expression of YKT6 protein in lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
图3. YKT6蛋白在肺腺癌和肺鳞癌中高表达
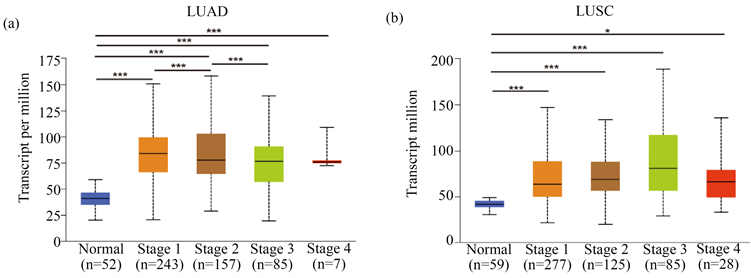
Figure 4. Correlation between YKT6 and the staging of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
图4. YKT6与肺腺癌和肺鳞癌疾病分期的相关性
 (a)~(c) 肺癌患者的OS、FP和PPS;(d)和(e) 肺腺癌患者的OS和RFS;(f) (g) 肺鳞癌患者的OS和RFS
(a)~(c) 肺癌患者的OS、FP和PPS;(d)和(e) 肺腺癌患者的OS和RFS;(f) (g) 肺鳞癌患者的OS和RFS
Figure 5. Correlation between YKT6 and prognosis of lung cancer
图5. YKT6与肺癌预后的相关性
4. 讨论
肺癌是世界上最常见的癌症之一 [8]。其中,NSCLC是最为常见的类型。超过七成的肺癌患者在确诊时,已处于局部晚期或晚期阶段,这使得部分患者初诊时已失去手术机会 [9]。目前的化疗药物缺乏特异性、副作用较大,在临床中已陷入治疗“瓶颈”,肺癌患者亟需更为有效、及时、个性化的治疗 [10]。
YKT6是一种进化高度保守的SNARE蛋白,可调节高尔基体膜融合 [11]。与其他SNARE蛋白不同,YKT6没有跨膜结构域,但在羧基端具有保守的串联半胱氨酸基序 [12]。最近研究表明,YKT6的高表达与乳腺癌的侵袭有关 [13]。此外,YKT6也可作为口腔鳞状细胞癌预后和免疫治疗反应的潜在预测指标,与细胞侵袭、转移和CD8+T细胞浸润有关 [14]。
在本研究中,我们下载了TCGA数据库中肿瘤的转录组数据以及临床信息,使用R语言进行分析,探究YKT6在各种恶性肿瘤组织中的表达情况。结果表明,YKT6在膀胱尿路上皮癌、乳腺浸润癌等18种癌症中高表达,这也为YKT6在各种癌症中的研究奠定了基础。基于Ualcan和HPA数据库发现:无论是LUAD还是LUSC,YKT6基因和蛋白表达水平均高于正常组织及癌旁组织。越来越多的证据表明,肿瘤细胞释放过量的外泌体,影响肿瘤的发生、发展、转移和耐药,而YKT6与外泌体的生成和释放有关 [15]。因此,我们推测YKT6可能通过调节外泌体的形成与释放进而参与于NSCLC的发生与进展。Xu等人研究发现,YKT6的高表达与LIHC的进展密切相关,可作为判断其预后不良的潜在生物学标志 [16]。目前尚未有YKT6与NSCLC预后的关系的报道,我们的分析结果表明,YKT6表达与LUAD的OS显著相关;YKT6对LUAD和LUSC均具有一定的诊断价值。然而,尽管有以上结果,但我们的研究仍有一部分局限性,我们仅仅通过在生物信息学网站进行了一些分析和验证,缺乏更深入的体内和体外实验,这些都是我们在后期需要加以改正的地方。但本研究是经过反复分析验证,结果是准确的,为NSCLC的机制的探索提供了新的方向。
以上结果表明,YKT6在NSCLC中表达上调,与NSCLC患者的临床病理学特征和预后相关,可作为NSCLC潜在的诊断和预后生物标志物。靶向YKT6可能是未来NSCLC治疗的新方向。
基金项目
国家自然科学基金青年基金(81802290, 81800182);山东省自然科学基金(ZR2018BH020)。
NOTES
*通讯作者。