1. 引言
眼睑痉挛是一种局限性肌张力障碍,患者眼睛周围的肌肉频繁不断的不自主收缩,导致眼睑闭合和视力障碍,影响日常生活和工作。严重的眼睑痉挛可能引起交通事故 [1] 。由于特发性眼睑痉挛的发病机制不明,目前的治疗主要是缓解症状 [2] 。许多治疗方法,如生物反馈、催眠、针灸、心理疗法都已经在临床试用过,但收效甚微。一些药物如左旋多巴,丁苯那嗪、安定、氯硝西泮、碳酸锂、哌啶醇、苯妥英、盐酸金刚烷胺也一直临床试用,以期缓解痉挛症状,但效果很差 [3] 。根据临床经验,我们在临床实践中使用右美沙芬治疗眼睑痉挛,发现右美沙芬对眼睑痉挛患者缓解症状有效,因此我们在此回顾性分析该系列病例。
2. 病例和方法
病例:2014年一位男性眼睑痉挛患者向我们反映,他偶然发现,当他得了上呼吸道感染后服用非处方镇咳药右美沙芬,其眼睑痉挛症状得到明显减轻。2015年1月至2016年12月期间,22例特发性眼睑痉挛患者在我科门诊接受右美沙芬治疗,30 mg每日三次口服,4周为一疗程。十五女性患者,七个男性患者,年龄在42至67岁之间(平均58.3岁),均由神经外科专家排除其它疾患确诊为特发性眼睑痉挛,排除严重内脏功能障碍和精神病,排除颅神经手术史。右美沙芬治疗期间,禁用其他用药,除非高血压、糖尿病患者长期使用的降压、降糖药。治疗前一周、治疗过程中每一周及治疗后一周,根据扬科维奇评分(Jankovic Rating Scale, JRS)和眼睑痉挛的残疾指数(Blepharospasm Disability Index, BSDI),评价眼睑痉挛的程度。同时记录任何副作用。
JRS:该评分表由神经外科医生评估 [4] ,该量表包括严重程度和频率两方面。严重程度方面,得分0意味着没有痉挛,得分1意味着只有在外部刺激下才出现眨眼增加,得分2意味着轻度自发的眼睑抽动,得分3意味着中度痉挛,得分4意味着严重痉挛。作为频率方面,0分意味着没有痉挛,1分意味着增加的闭眼频率,2分意味着眼睑轻度抽搐,但持续 < 1秒,得分3意味着眼睑痉挛持续 > 1秒,4分意味着因持续闭目而功能性失明。因此,JRS总分为8。
BSDI:BSDI是患者自评量表 [4] 。它包括6个项目,即驾驶车辆,阅读,看电视,购物,散步和做日常活动。对于每一个项目,得分0意味着没有障碍,得分1意味着轻微的障碍,得分2意味着中度障碍,得分3意味着严重的障碍,得分4意味着完全不能做这项活动。如果一个项目不适用于一个病人,例如,一个没有驾驶执照的病人“驾驶车辆”的项目,该项目应该被删除。最后分数是所有适用活动得分的平均分数。因此,BSDI得分范围是0~4。
统计分析:t检验和方差分析用于定量数据分析。P < 0.05者有统计学意义。
3. 结果
表1列明了22例眼睑痉挛患者在不同时间点的JRS和BSDI评分。
右美沙芬治疗前我们检测了患者的基线评分,JRS基线评分是5.55 ± 1.10分,BSDI基线评分为2.87 ± 0.59。
表1. 22例特发性眼睑痉挛患者接受右美沙芬治疗的JRS和BSDI评分
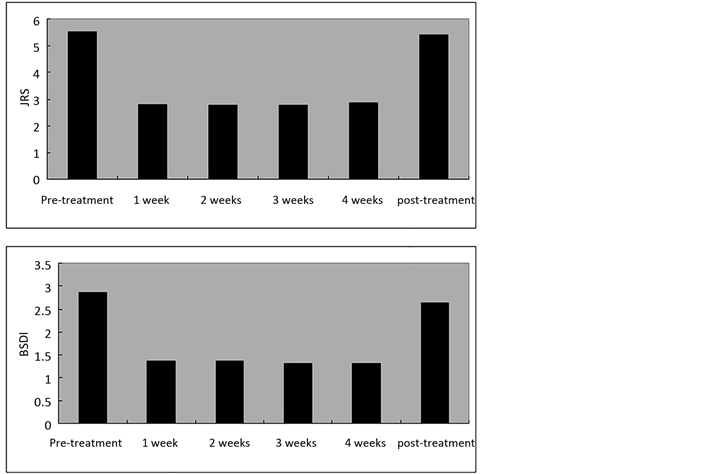
Figure 1. The mean JRS and BSDI scores of essential blepharospasm patients treated with dextromethorphan
图1. 特发性眼睑痉挛患者右美沙芬治疗的平均JRS和BSDI评分
右美沙芬治疗1周后,JRS评分下降到2.82 ± 0.85分,BSDI下降到1.36 ± 0.58分。与治疗前基线相比,JRS (P < 0.05)和BSDI (P < 0.05)的改善都具有统计学意义。
如图1所示,在接下来的3周的治疗,JRS和BSDI得分保持在一个稳定的状态,没有显著性改变 (P > 0.05)。
停止右美沙芬治疗一周后,JRS评分(5.41 ± 1.01分)和BSDI评分(2.63 ± 0.64分)回到治疗前的基线水平。
本组无严重并发症。两名患者有轻度头晕,1例有轻度恶心,这些副作用是可耐受的,并未导致右美沙芬停药。
4. 讨论
由于特发性眼睑痉挛的发病机制尚不清楚,当前治疗的主要目的是缓解痉挛症状。
最常见的治疗方法是A型肉毒毒素注射。肉毒杆菌毒素治疗特发性眼睑痉挛的短期表现是很成功的,其不良事件少见。但是肉毒杆菌神经毒素对于机体免疫系统是一种外源性抗原,会引发特异性抗体的产生,最终肉毒杆菌毒素将被中和。因此,肉毒杆菌神经毒素注射一般开始是有效的,但会在几年内耐药 [5] 。
特发性眼睑痉挛的手术治疗效果不理想。脑深部电刺激(DBS),部分面神经切断术,面肌悬吊术都曾在临床尝试,在某种程度上缓解症状,但不能治愈 [6] 。
如上所述,各种口服药物的症状缓解效果非常有限。我们偶然从临床实践发现,镇咳药右美沙芬能抑制眼睑痉挛。这可能成为非手术治疗的新选择,当然需要未来前瞻性的临床试验。
作为镇咳药,右美沙芬可能是作用于中枢神经系统以提高咳嗽阈值 [7] 。它能减轻谷氨酸诱导的神经毒性,对缺血引起的脑损伤具有神经保护作用 [8] 。右美沙芬还有许多其他医疗应用,如疼痛缓解,精神疾病治疗,以及成瘾的治疗 [9] 。
右美沙芬的药理作用十分广泛。它是一种非选择性5-羟色胺再摄取抑制剂和σ-1受体激动剂,也是一个低亲和力的非竞争性NMDA受体(NMDA受体)拮抗剂 [10] 。它能抑制突触前末梢投射到二级神经元的谷氨酸释放 [11] 。虽然右美沙芬在中枢神经系统中具有广泛的药理作用,但确切的作用点和作用机制尚不完全清楚。已被证明在眼睑痉挛患者中,很多大脑区域功能异常,包括基底神经节,皮层和小脑。然而,目前尚不清楚这些部位的功能变化是否是该病的病因或结果 [2] 。参与特发性眼睑痉挛发病的神经回路和确切机制尚不明确,因此研究右美沙芬如何治疗眼睑痉挛还有很大的空间。
作为一项回顾性分析,本文存在局限:只有治疗前后的自身对照,没有随机对照。在将来的前瞻性研究中需要克服该缺陷。
5. 结论
本研究发现右美沙芬对眼睑痉挛患者有效,并且无明显严重副作用。这一发现可能意味着另一种治疗选项。
基金项目
本研究得到上海市科委项目(14DZ1930303)的资助。